ZYGOMATIC BONE ANATOMY
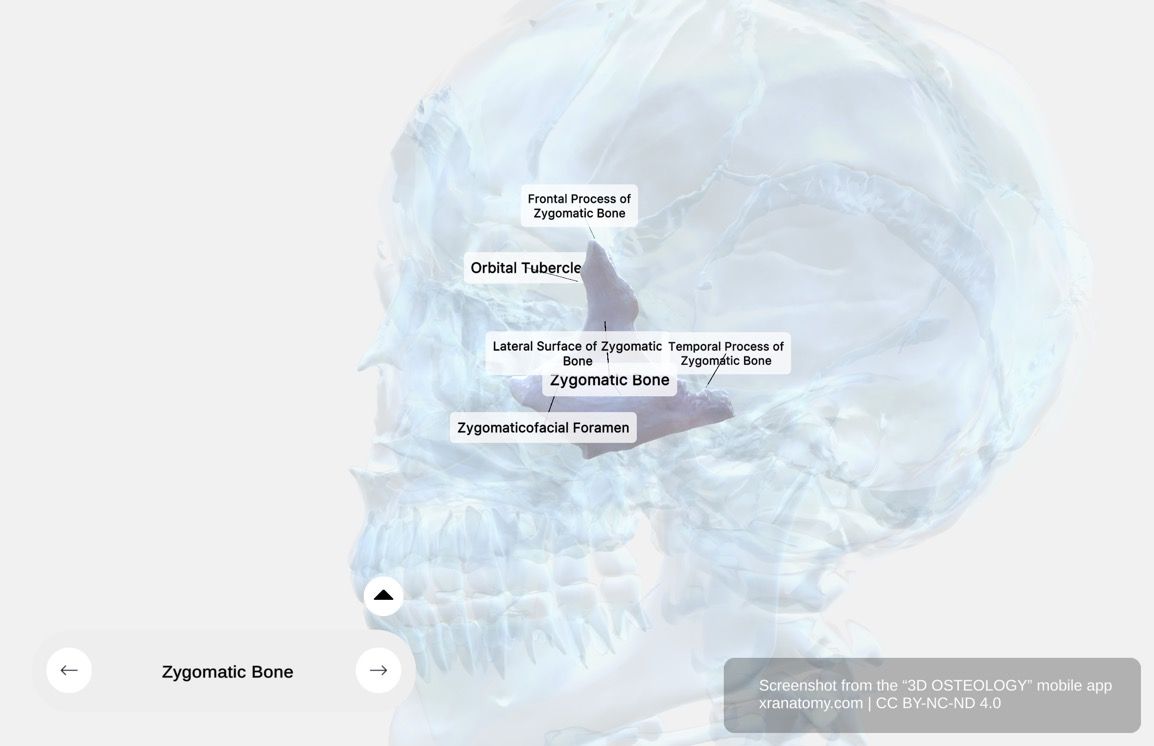
Zygomatic Bone - General Structure, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The zygomatic bone is the foundation of your cheek. Understanding its three surfaces, key foramina, and articulations helps you see how this single bone shapes your facial contour, protects your eye, and anchors your chewing muscles.
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
The zygomatic bone is a paired facial bone with a diamond-shaped configuration. Commonly referred to as your cheekbone, it creates the prominent contour of your cheek region. It contributes to the lateral orbital wall and orbital floor. The zygomatic bone provides stable support to your facial framework, facilitates your facial expression movements, and offers protection to your ocular structures.
Articulations
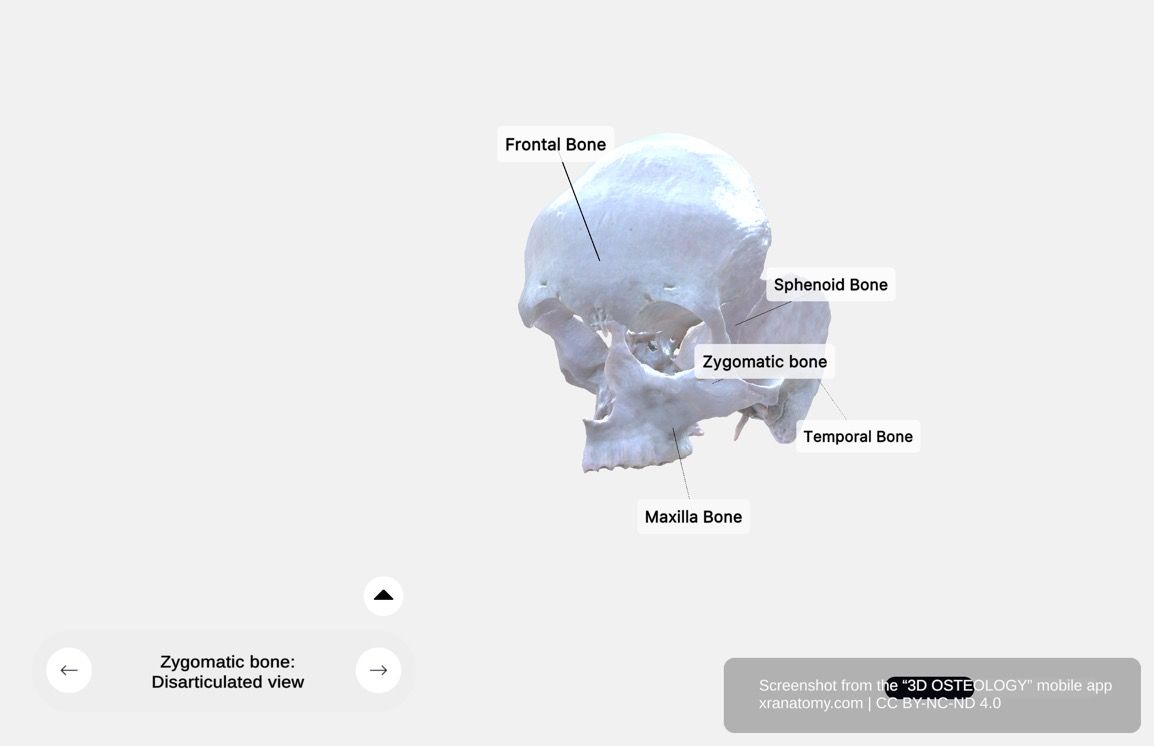
Zygomatic Bone - Articulations, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
Articulating Bones
The zygomatic bone articulates with four bones: the frontal bone, the sphenoid bone, the maxilla, and the temporal bone.
Functional Significance
The zygomatic bone provides the structural prominence of your cheek, defining your facial contour. It forms part of the lateral orbital wall and floor, protecting your eye. It contributes to the zygomatic arch alongside the temporal bone, providing attachment for your masseter muscle. It also transmits branches of the zygomatic nerve (from V2) to supply sensation to your cheek and temple.
LATERAL SURFACE

Zygomatic Bone - Lateral Surface, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The lateral surface has a convex and smooth external aspect. It constitutes the outer surface of your cheek. Its key feature is the zygomaticofacial foramen.
Zygomaticofacial Foramen
The zygomaticofacial foramen is a small aperture on the lateral surface. It transmits the zygomaticofacial nerve and accompanying blood vessels, supplying your facial structures.
FRONTAL PROCESS
The frontal process is a thin elongated bony projection that extends in a superior direction. It articulates with the frontal bone superiorly and contributes to the formation of the lateral orbital wall. It also provides attachment sites for your facial musculature. Its key landmark is the orbital tubercle.
Orbital Tubercle
The orbital tubercle is a bony elevation on the frontal process. It serves as an attachment for the lateral palpebral ligament, the suspensory ligament of the eye, and part of the aponeurosis of levator palpebrae superioris.
TEMPORAL PROCESS
The temporal process projects in a posterior direction and unites with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone. Together they form the zygomatic arch. This arch is significant for attachment of your masticatory muscles.
TEMPORAL SURFACE
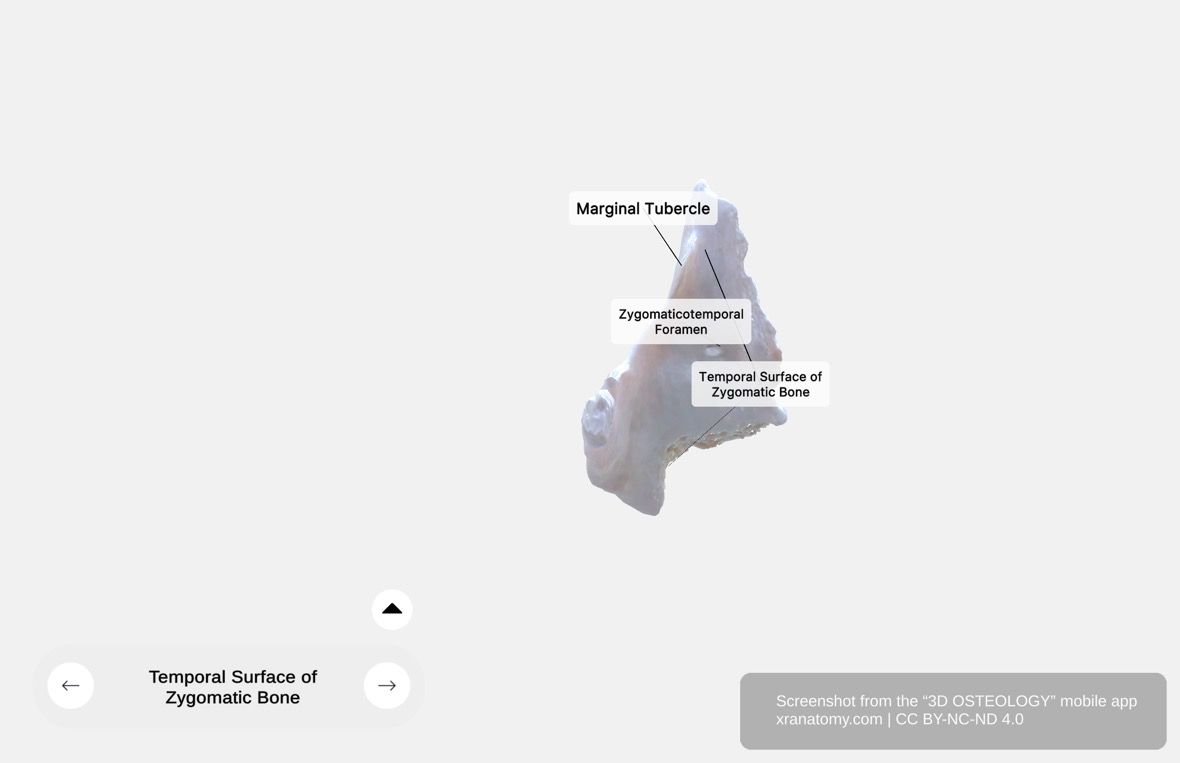
Zygomatic Bone - Temporal Surface, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The temporal surface is the inner aspect oriented toward the temporal bone. It is concave in configuration and contributes to the temporal fossa and infratemporal fossa formation. Its key features include the zygomaticotemporal foramen and the marginal tubercle.
Zygomaticotemporal Foramen
The zygomaticotemporal foramen is an opening on the temporal surface. It transmits the zygomaticotemporal nerve, which provides sensory supply to the skin of your temple.
Marginal Tubercle
The marginal tubercle is a raised prominence located on the posterior border of the frontal process. It provides attachment for the temporal fascia.
ORBITAL SURFACE

Zygomatic Bone - Orbital Surface, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The orbital surface forms a substantial portion of the lateral orbital wall and contributes to the orbital floor. It provides protective covering for your eye and has a smooth bony surface. Its key feature is the zygomatico-orbital foramen.
Zygomatico-orbital Foramen
The zygomatico-orbital foramen is an aperture on the orbital surface. It permits the passage of zygomatic nerve branches and opens into the orbital cavity.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Name the four bones the zygomatic bone articulates with.
Reveal Answer
Frontal bone, sphenoid bone, maxilla, and temporal bone.
2. What are the three foramina of the zygomatic bone and on which surface is each located?
Reveal Answer
The zygomaticofacial foramen is on the lateral surface, the zygomaticotemporal foramen is on the temporal surface, and the zygomatico-orbital foramen is on the orbital surface. All three transmit branches of the zygomatic nerve.
3. Which two bones unite to form the zygomatic arch?
Reveal Answer
The temporal process of the zygomatic bone and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone unite to form the zygomatic arch.
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you understand the zygomatic bone and its surfaces, processes, and foramina, the next page focuses on the Lacrimal Bone. You will explore lacrimal bone anatomy with interactive 360-degree 3D views.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.