VOMER BONE ANATOMY
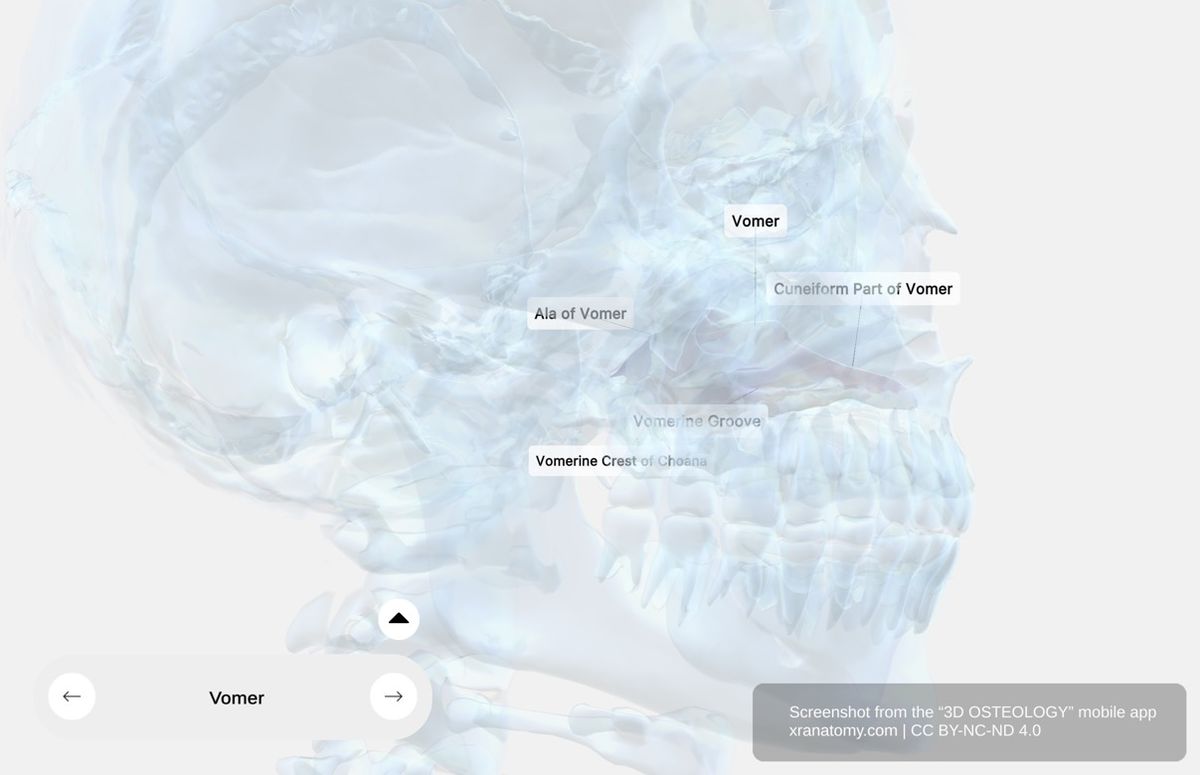
Vomer Bone - X-ray View, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The vomer is a thin, unpaired bone that forms the inferior part of your nasal septum. Understanding its borders, surfaces, and articulations helps you see how this single midline bone divides your nasal passages and anchors to the sphenoid, maxillae, palatine bones, and ethmoid above and below.
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
The vomer is a thin unpaired bone located in the midsagittal plane. It constitutes the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum and functions to divide your left and right nasal passages. The vomer is essential for nasal cavity structure and function.
ARTICULATIONS
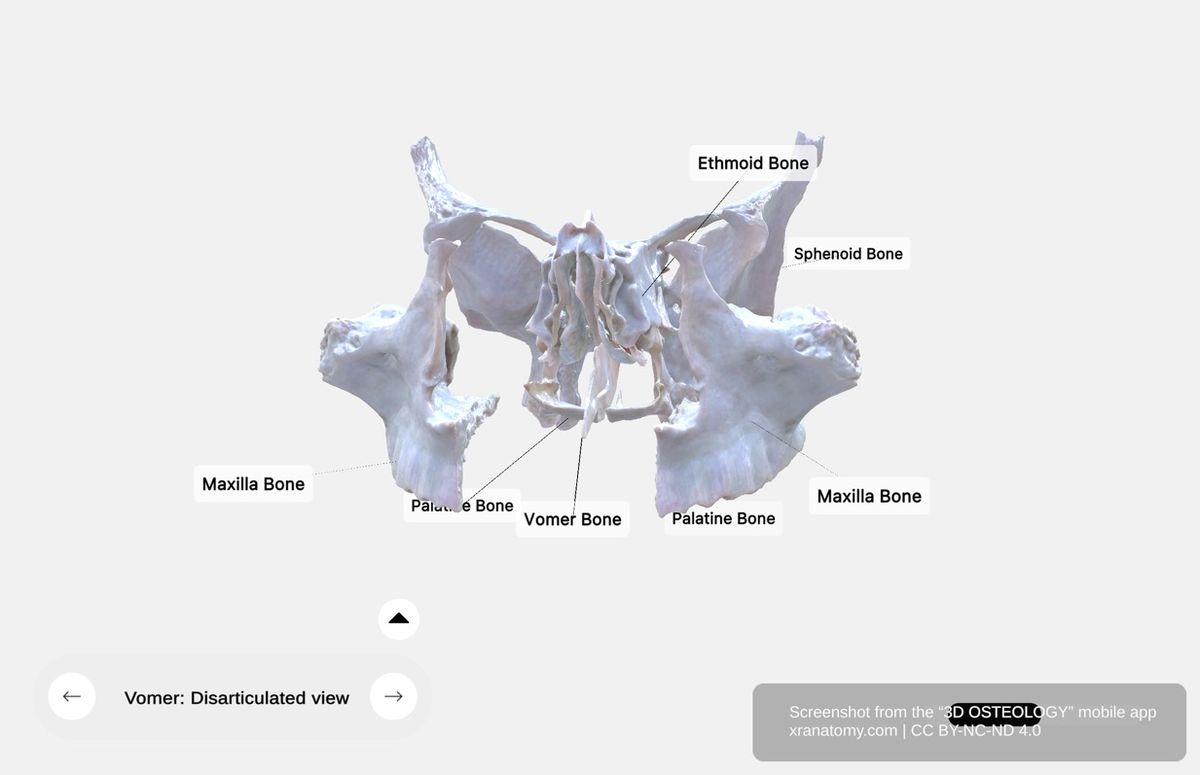
Vomer Bone - Disarticulated View, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The vomer connects with multiple cranial and facial bones: the sphenoid bone, the paired maxillae, the paired palatine bones, and the ethmoid bone.
SUPERIOR BORDER
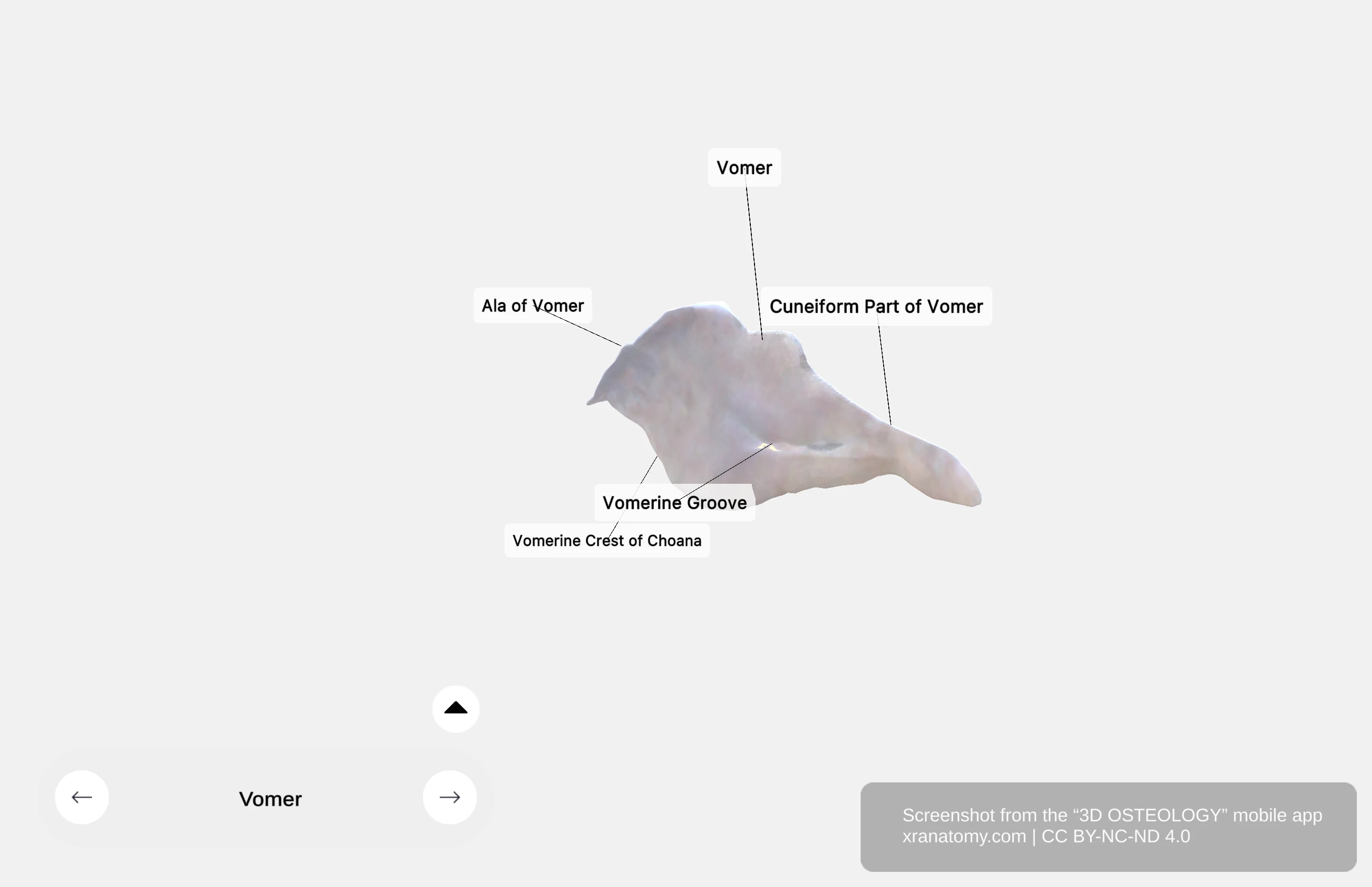
The superior border of the vomer features the alae of the vomer, bilateral wing-like extensions that anchor the bone within your skull.
Alae of Vomer
The alae are bilateral wing-like extensions that project laterally from the superior margin. They articulate with the sphenoidal conchae, the vaginal processes of the medial pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bone, and with the palatine bones via the sphenoidal processes. These connections anchor the vomer securely within your skull.
SURFACES
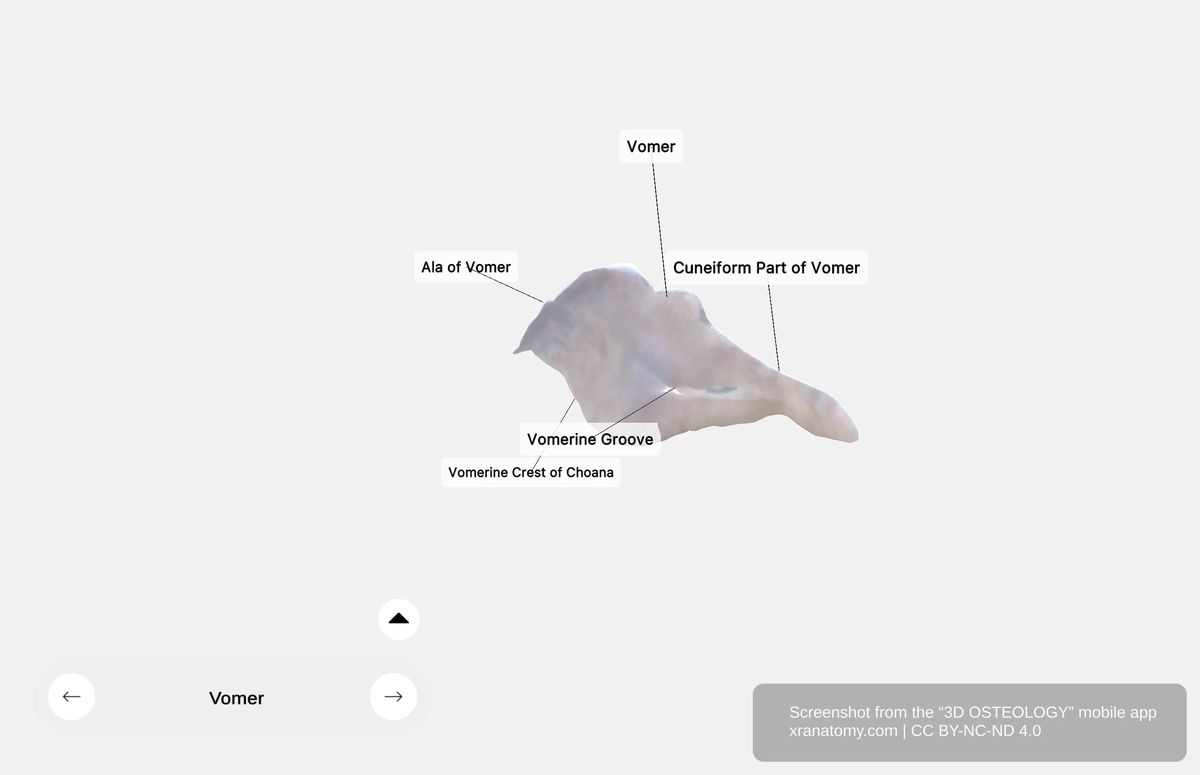
The surfaces of the vomer feature the vomerine groove, an oblique indentation that accommodates neurovascular structures.
Vomerine Groove
The vomerine groove is an oblique indentation on the bone surface. It provides passage for blood vessels and accommodates nerves supplying your nasal septum.
POSTERIOR BORDER
The posterior border of the vomer features the vomerine crest of the choana, which contributes to the formation of the posterior nasal openings.
Vomerine Crest of Choana
The vomerine crest is a posterior margin feature of the vomer. It contributes to the formation of the choanae, which serve as openings between your nasal cavity and nasopharynx.
ANTERIOR ASPECT
The anterior aspect of the vomer features the cuneiform part, a wedge-shaped region that connects to the ethmoid bone and septal cartilage.
Cuneiform Part
The cuneiform part is the wedge-shaped anterior portion of the vomer. It articulates with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and connects with the septal cartilage, completing your nasal septum.
FUNCTIONAL SIGNIFICANCE
The vomer ensures proper separation of your nasal passages. It is critical for efficient airflow through your nose by directing airflow through both nasal passages.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What four bones does the vomer articulate with?
Reveal Answer
The sphenoid bone, paired maxillae, paired palatine bones, and the ethmoid bone.
2. What are the alae of the vomer, and what do they articulate with?
Reveal Answer
The alae are bilateral wing-like extensions from the superior margin. They articulate with the sphenoid bone via the vaginal processes and with the palatine bones via the sphenoidal processes.
3. What structure does the vomerine groove accommodate?
Reveal Answer
The vomerine groove provides passage for blood vessels and nerves supplying the nasal septum.
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you understand the vomer and its role in the nasal septum, the next page focuses on the Zygomatic Bone. You will explore zygomatic bone anatomy with interactive 360-degree 3D views, covering its processes, surfaces, and articulations that form the prominence of your cheek.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.