PARIETAL BONE ANATOMY
Parietal Bone - Articulations, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The parietal bones form a substantial portion of your cranial vault, protecting the brain beneath. Understanding their external and internal surfaces, four borders, and four angles helps you see how these paired flat bones connect with the frontal, occipital, and temporal bones through major cranial sutures.
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Overview
The parietal bones are paired flat bones of your cranium, located on the superolateral aspect of your skull. They form a substantial portion of your cranial vault, contributing to both the sides and roof of your skull. The parietal bones provide protection for your underlying brain.
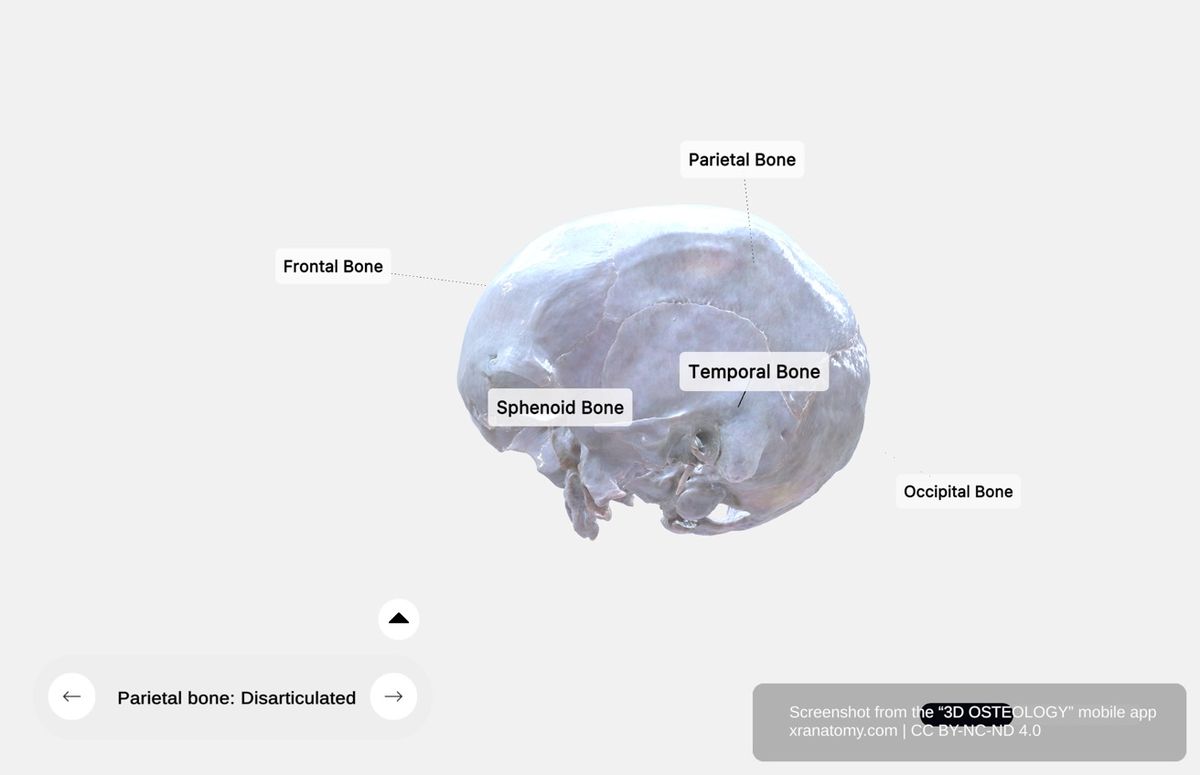
Articulations
Each parietal bone articulates with the frontal bone anteriorly, the occipital bone posteriorly, the temporal bone inferiorly, the greater wing of the sphenoid at the anteroinferior angle, and the opposite parietal bone medially at the sagittal suture.
EXTERNAL SURFACE
External Surface of the Parietal Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
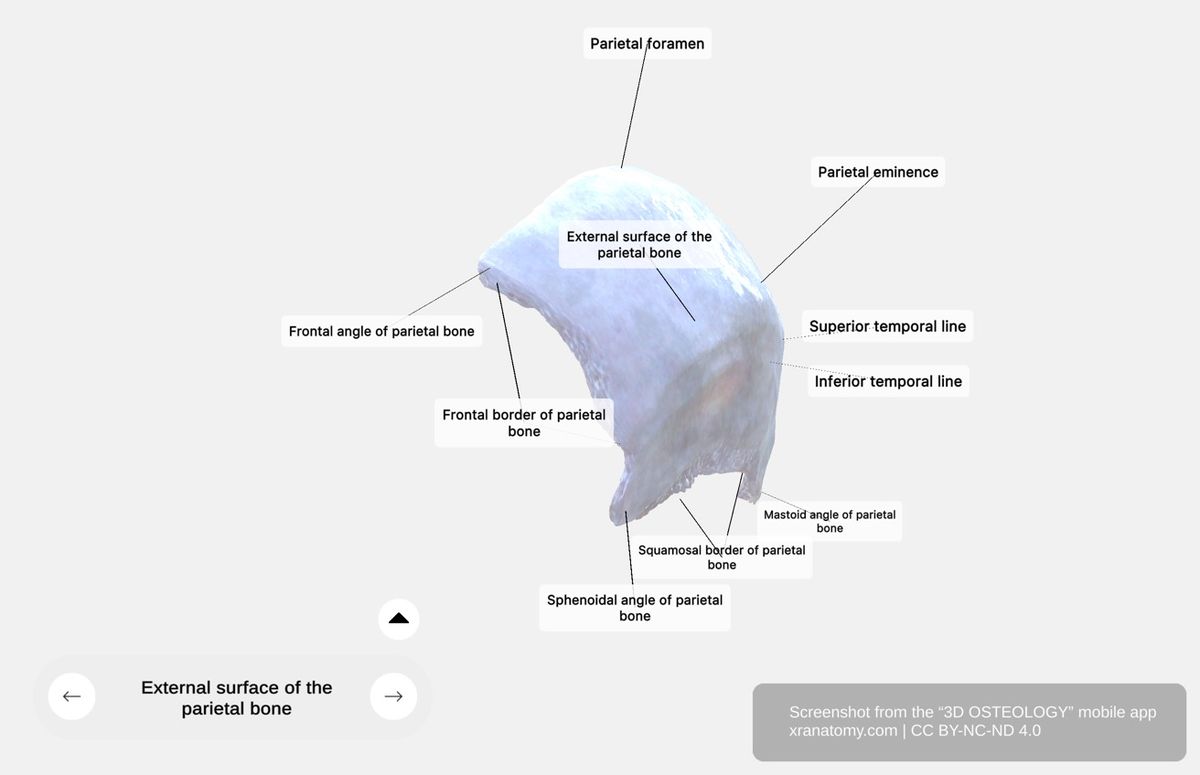
The external surface has a smooth convex contour and forms the structural foundation beneath your scalp. Its key landmarks include the parietal eminence near the center, two curved ridges called the temporal lines, and the parietal foramen near the sagittal border.
Parietal Eminence
The parietal eminence is a prominent convex region located near the center of the bone, also termed the parietal tuber. It contributes to your rounded skull contour.
Temporal Lines
The superior temporal line is a curved ridge that arches across the external surface. It serves as the attachment site for temporal fascia.
The inferior temporal line is a curved ridge that runs parallel below the superior line. It serves as the attachment site for the temporalis muscle, which is involved in your mastication.
Parietal Foramen
The parietal foramen is a small aperture located near the sagittal border. It is variable in size and transmits an emissary vein.
INTERNAL SURFACE

Internal Surface of the Parietal Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The internal surface contains grooves and depressions that accommodate your brain structures and meninges. Its key features include the groove for the middle meningeal artery and additional surface markings from arachnoid granulations and cerebral gyri.
Groove for Middle Meningeal Artery
The groove for the middle meningeal artery is a prominent channel that allows the artery to pass across the inner bone surface. The middle meningeal artery supplies your dura mater, which is the outermost meningeal layer.
Additional Surface Markings
The internal surface also shows impressions from arachnoid granulations and impressions from cerebral gyri.
BORDERS AND SUTURES
Borders and Angles of the Parietal Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The parietal bone has four borders, each forming a distinct cranial suture. The sagittal border connects with the opposite parietal bone, the frontal border articulates anteriorly with the frontal bone, the occipital border articulates posteriorly with the occipital bone, and the squamosal border articulates inferiorly with the temporal bone and greater wing of the sphenoid.
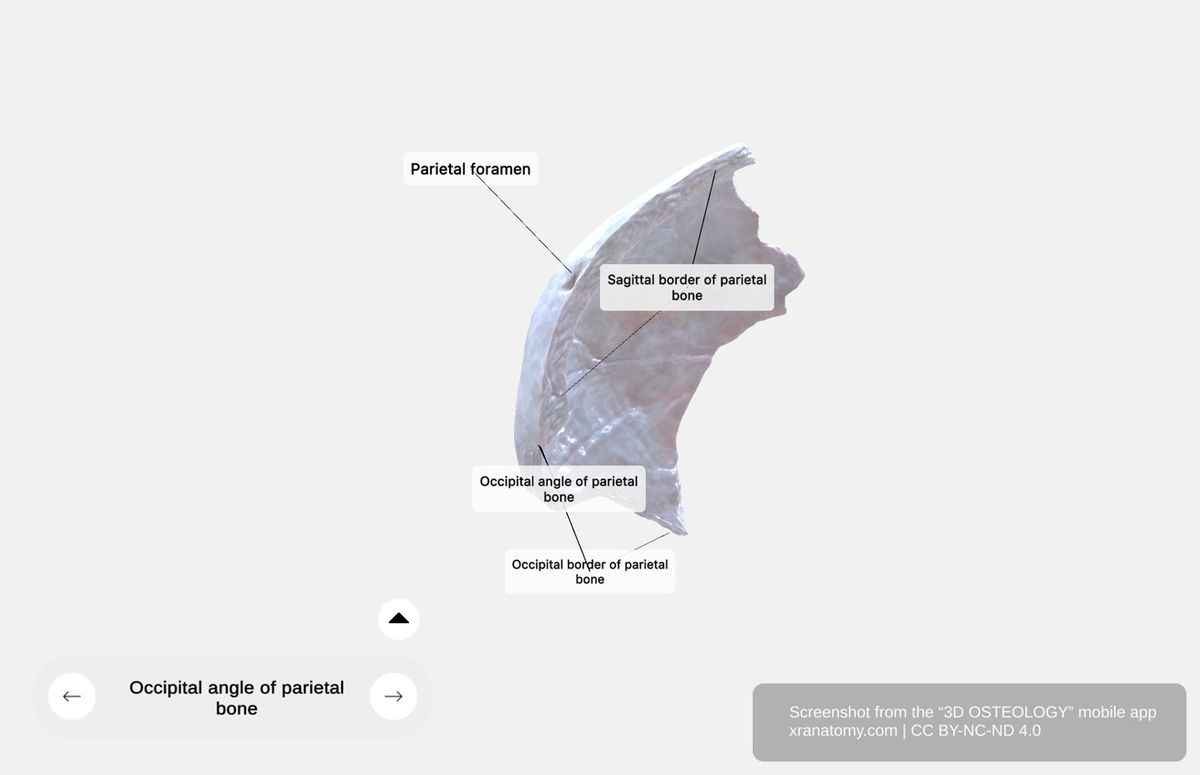
Sagittal Border
The sagittal border is the longest border. It connects with the opposite parietal bone and forms the sagittal suture.
Frontal Border
The frontal border is the anterior border. It articulates with the frontal bone and forms the coronal suture.
Occipital Border
The occipital border is the posterior border. It articulates with the occipital bone and forms the lambdoid suture.
Squamosal Border
The squamosal border is the inferior border. Its anterior portion articulates with the greater wing of the sphenoid, its central portion articulates with the squamous part of the temporal bone, and its posterior portion articulates with the mastoid part of the temporal bone.
ANGLES
The parietal bone has four angles at its border junctions. These are the frontal angle at the anterosuperior corner, the occipital angle at the posterosuperior corner, the sphenoidal angle at the anteroinferior corner, and the mastoid angle at the posteroinferior corner.
Frontal Angle
The frontal angle is the anterosuperior corner, located at the intersection of the sagittal and coronal sutures.
Occipital Angle
The occipital angle is the posterosuperior corner, located at the junction of the sagittal and lambdoid sutures.
Sphenoidal Angle
The sphenoidal angle is the anteroinferior corner, where the bone meets the frontal bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid.
Mastoid Angle
The mastoid angle is the posteroinferior corner. It articulates with the occipital bone and the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Name the four bones that each parietal bone articulates with.
Reveal Answer
The frontal bone (anteriorly), the occipital bone (posteriorly), the temporal bone (inferiorly), and the opposite parietal bone (medially at the sagittal suture).
2. What are the two temporal lines, and what does each attach to?
Reveal Answer
The superior temporal line is the attachment site for temporal fascia. The inferior temporal line is the attachment site for the temporalis muscle, which is involved in mastication.
3. Which border of the parietal bone is the longest, and what suture does it form?
Reveal Answer
The sagittal border is the longest border. It connects with the opposite parietal bone and forms the sagittal suture.
WHAT'S NEXT
Next, explore the Sphenoid Bone, a complex butterfly-shaped bone at the base of your skull. You will study its body, greater and lesser wings, pterygoid processes, and the sella turcica that houses the pituitary gland.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.