PATELLA ANATOMY
Patella - X-Ray View, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in your body. It protects your knee joint and enhances the leverage of your quadriceps muscle during knee extension. Understanding its surfaces, borders, and articulations helps you see how this small bone plays a key role in the mechanics of your lower limb.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
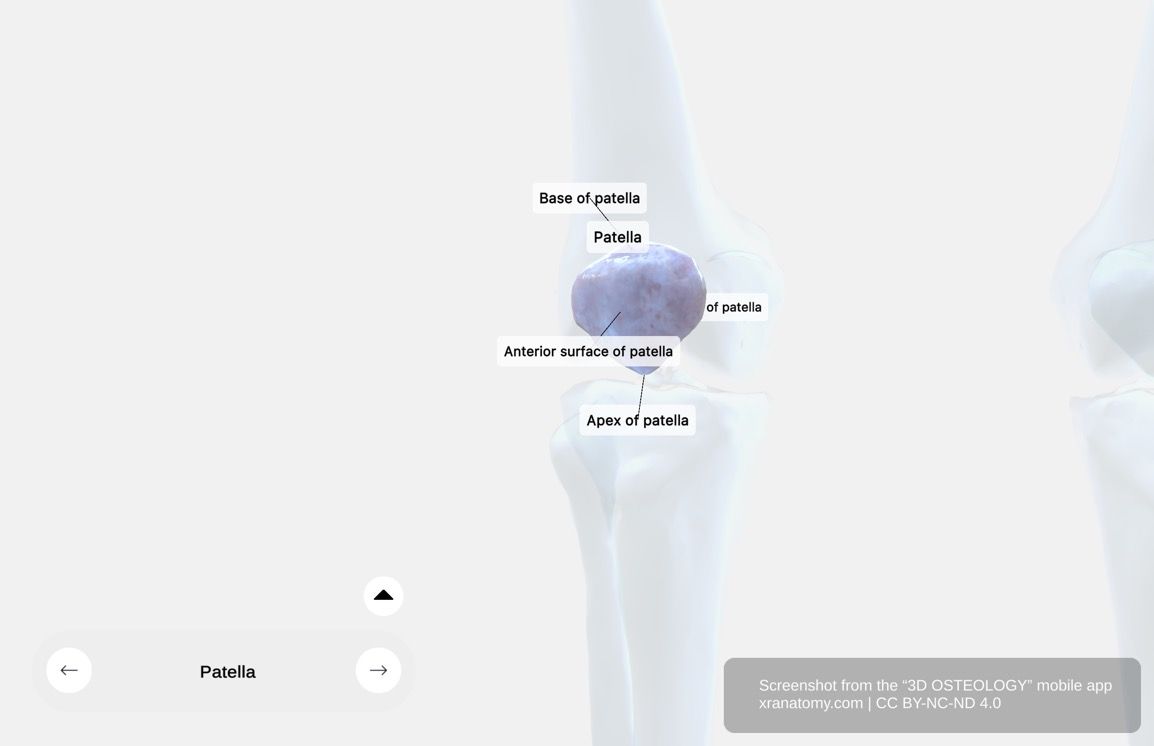
GENERAL STRUCTURE

Patella - General Structure, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in your body, characterized by its flat and triangular shape with an anterior and posterior surface, three borders, and an apex. Located in front of your knee joint, it sits embedded in the tendon of your quadriceps femoris. Below you will find details on its location, shape and characteristics, and functions.
Location
Your patella sits in front of your knee joint. It is embedded in the tendon of your quadriceps femoris muscle.
Shape and Characteristics
The patella has a flat and triangular shape. It features two surfaces (anterior and posterior), three borders, and an apex.
Functions
The patella serves two main roles. First, it provides protection by shielding your knee joint from external trauma. Second, it gives your quadriceps muscle a mechanical advantage by enhancing the leverage of the muscle during knee extension, which increases the efficiency of your leg straightening.
FEATURES
The patella has several distinct features. The base forms its upper border, the apex points downward, the articular surface sits on its posterior side, and the anterior surface faces outward beneath your skin.
Base (Superior Border)
The base is thick and slopes downwards and forwards, forming the upper border of the patella. It serves as the attachment site for parts of your quadriceps femoris muscle and receives your quadriceps tendon.
Apex
The apex is the pointed, lower part of the bone, directed inferiorly. It serves as the attachment site for the ligamentum patellae (patellar ligament), which connects your patella to your tibial tuberosity.
Articular Surface
The articular surface is located on the posterior side of the patella. It is a smooth, oval-shaped area divided into two facets by a vertical ridge. The lateral facet is larger than the medial facet. This surface articulates with the patellar surface of the femur, allowing smooth gliding during your knee movements. It is covered with hyaline cartilage for friction reduction.
Anterior Surface
The anterior surface is convex and has a rough texture. It is perforated by small holes for nutrient vessels and covered by expansions from your quadriceps tendon. This surface provides protection to your knee joint and serves as an attachment point for your quadriceps tendon. It is subcutaneous and palpable through your skin.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What type of bone is the patella, and where is it located?
Reveal Answer
The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in your body. It sits in front of your knee joint, embedded in the tendon of your quadriceps femoris muscle.
2. What divides the articular surface of the patella into two facets, and which facet is larger?
Reveal Answer
A vertical ridge divides the articular surface into two facets. The lateral facet is larger than the medial facet.
3. What structure attaches to the apex of the patella, and where does it connect?
Reveal Answer
The ligamentum patellae (patellar ligament) attaches to the apex. It connects the patella to your tibial tuberosity.
WHAT'S NEXT
Next, you will explore the Bones of the Foot. That page covers the 26 bones of your foot organized into three groups: 7 tarsal bones, 5 metatarsal bones, and 14 phalanges.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.