RIGHT VENTRICLE
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →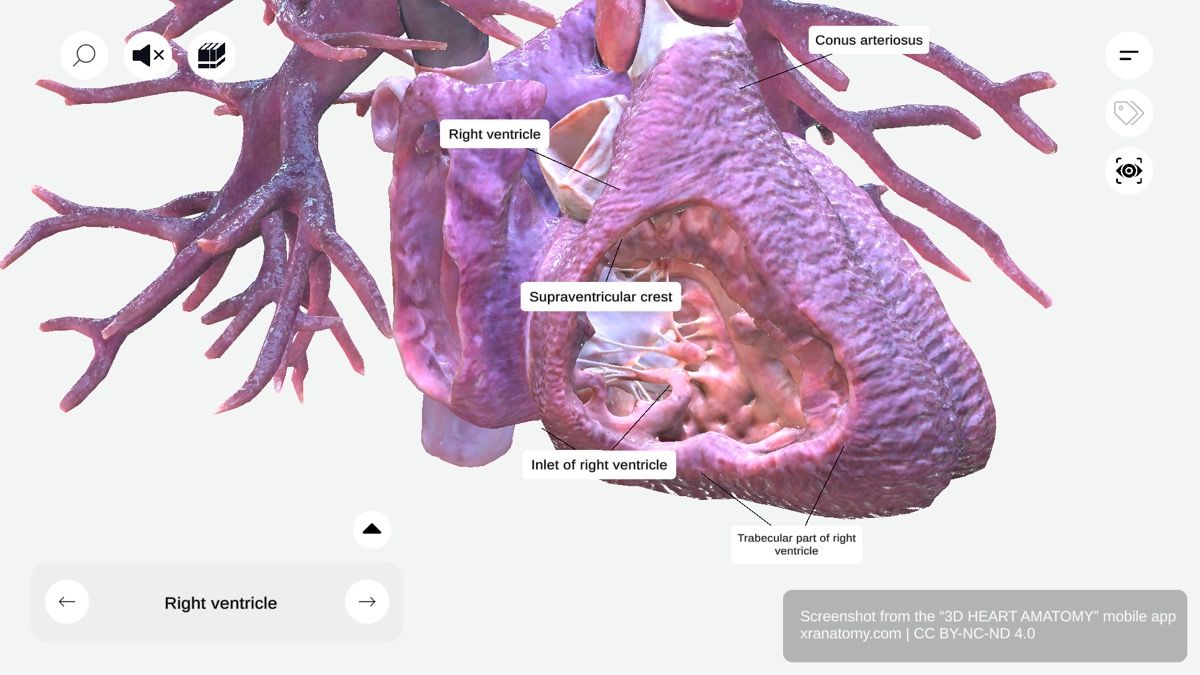
Right Ventricle - Overview, Preview from the app.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The right ventricle receives all the deoxygenated blood returning from your body and pumps it into your pulmonary circulation for oxygenation. Understanding its three components, valve apparatus, and muscular architecture helps you see how this chamber keeps blood flowing in one direction toward your lungs.
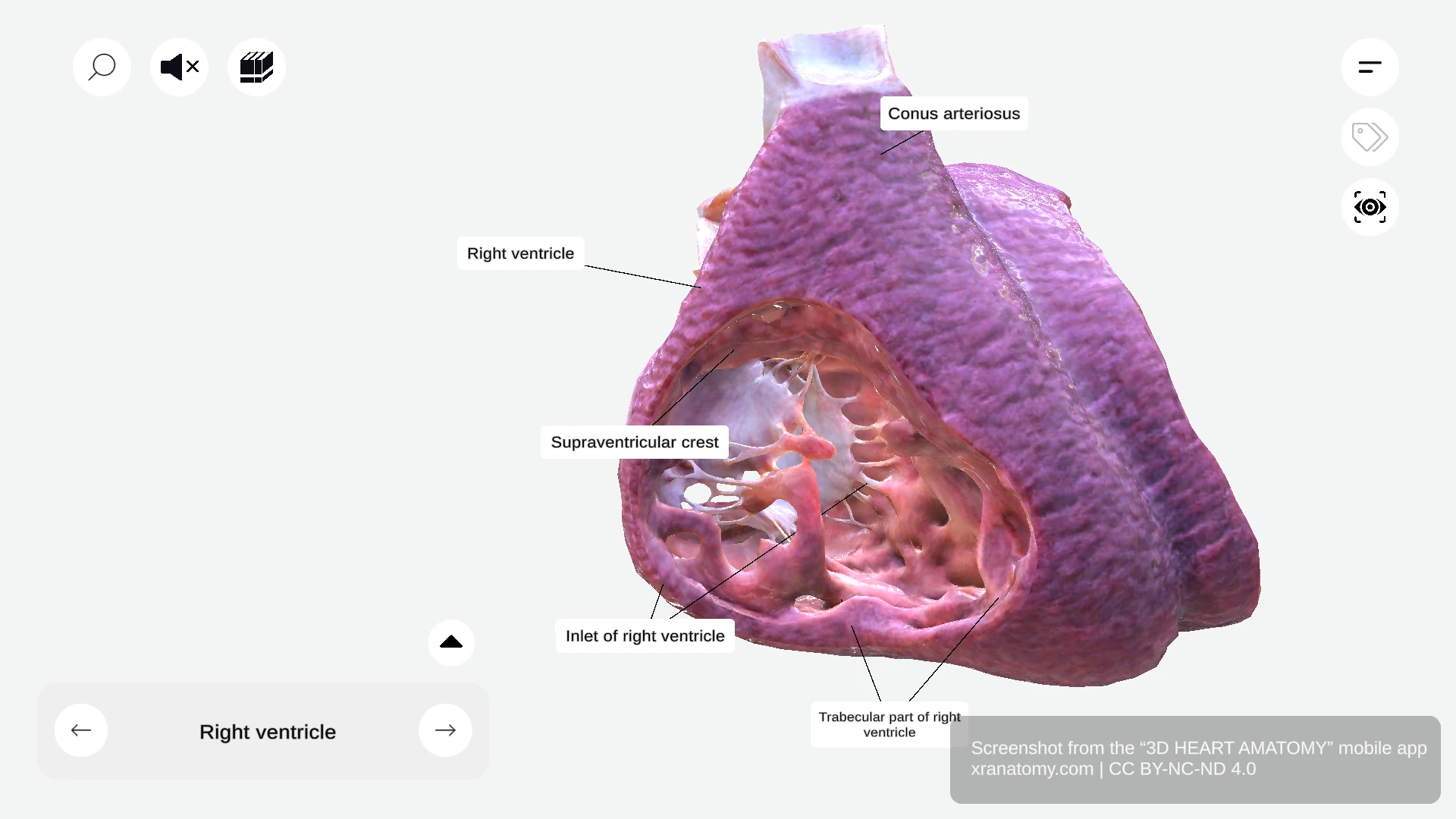
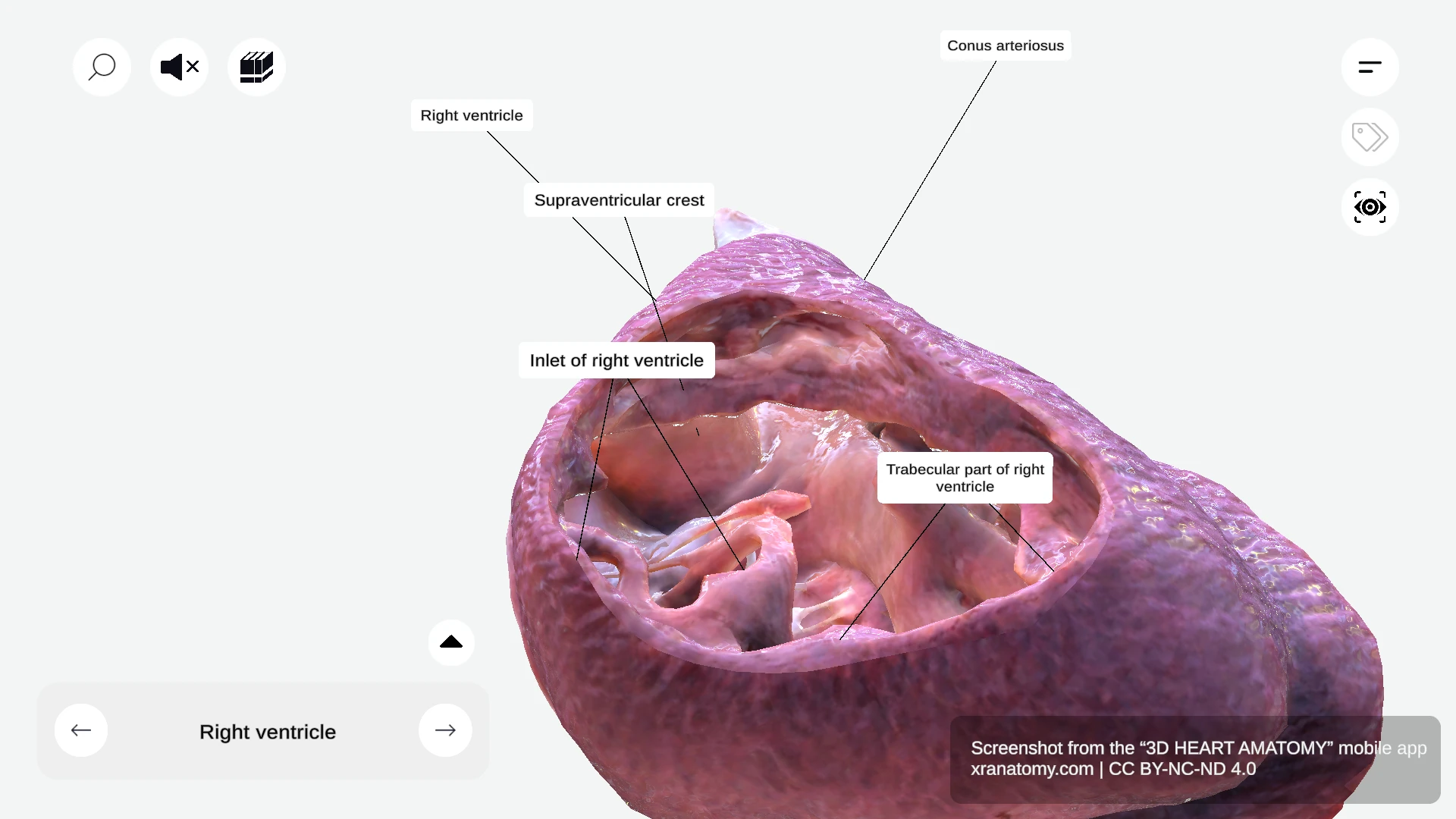
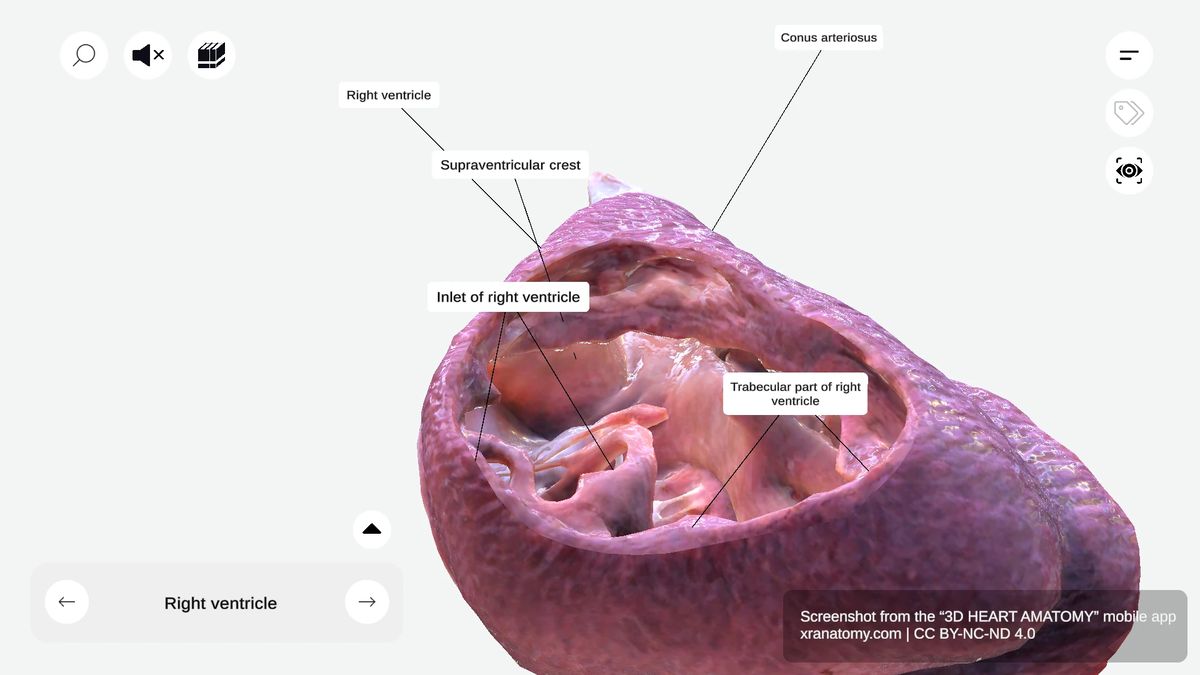
RIGHT VENTRICLE
The right ventricle is one of four cardiac chambers. It sits anteriorly and forms the majority of your heart's anterior surface. This chamber has a triangular shape, receives deoxygenated blood from your right atrium, and pumps it into your pulmonary circulation via the pulmonary artery.
Three Main Components
The right ventricle has three main components: the inlet, the trabecular part, and the outlet. Together, these components ensure efficient blood flow to your lungs for oxygenation.
INLET OF RIGHT VENTRICLE
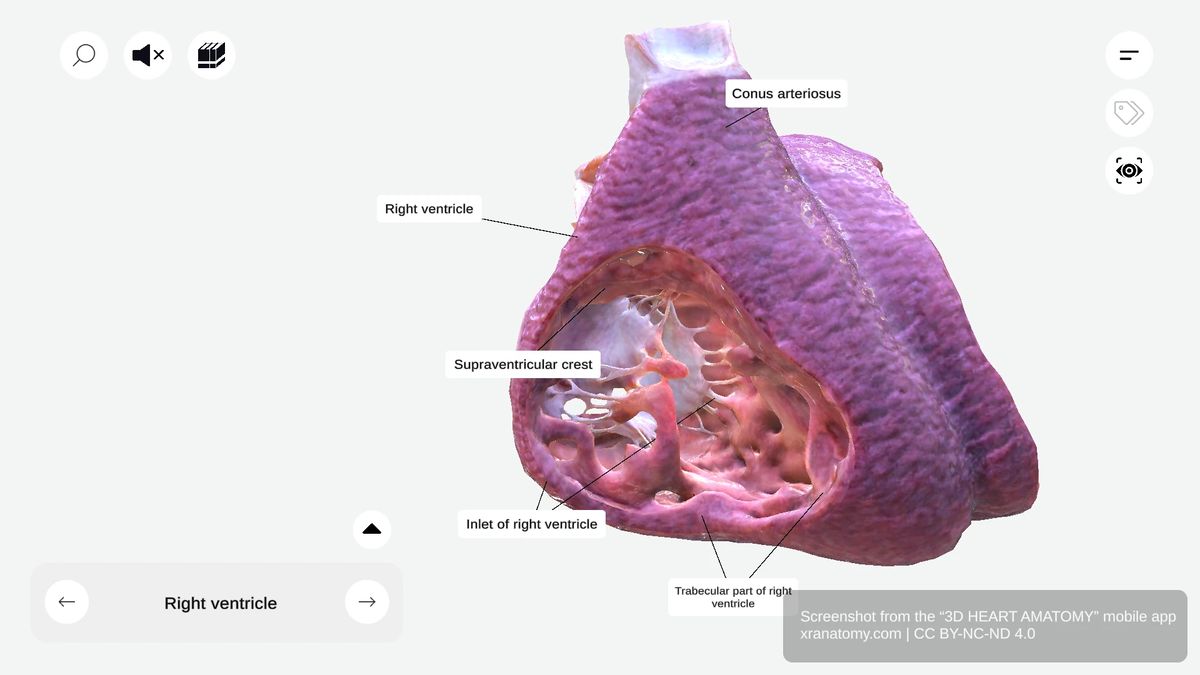
The inlet contains the tricuspid valve apparatus and ensures unidirectional blood flow from your right atrium. It prevents backflow during ventricular contraction. The inlet region features two key sub-structures: the tricuspid valve apparatus with its leaflets, chordae tendineae, and papillary muscles, and the supraventricular crest that separates inflow from outflow.
Tricuspid Valve Apparatus Components
The tricuspid valve apparatus consists of three components: tricuspid valve leaflets, chordae tendineae, and papillary muscles.
Supraventricular Crest
The supraventricular crest is a muscular ridge between the pulmonary and tricuspid valves. It separates your inflow and outflow tracts and directs blood flow efficiently through your heart.
OUTLET OF RIGHT VENTRICLE
Conus Arteriosus
The conus arteriosus, also known as the infundibulum, is a conical pouch in the upper right ventricle. It serves as the outflow component of the right ventricle and provides support for the pulmonary valve. The conus arteriosus ensures smooth blood flow into your pulmonary artery.
TRABECULAR PART OF RIGHT VENTRICLE
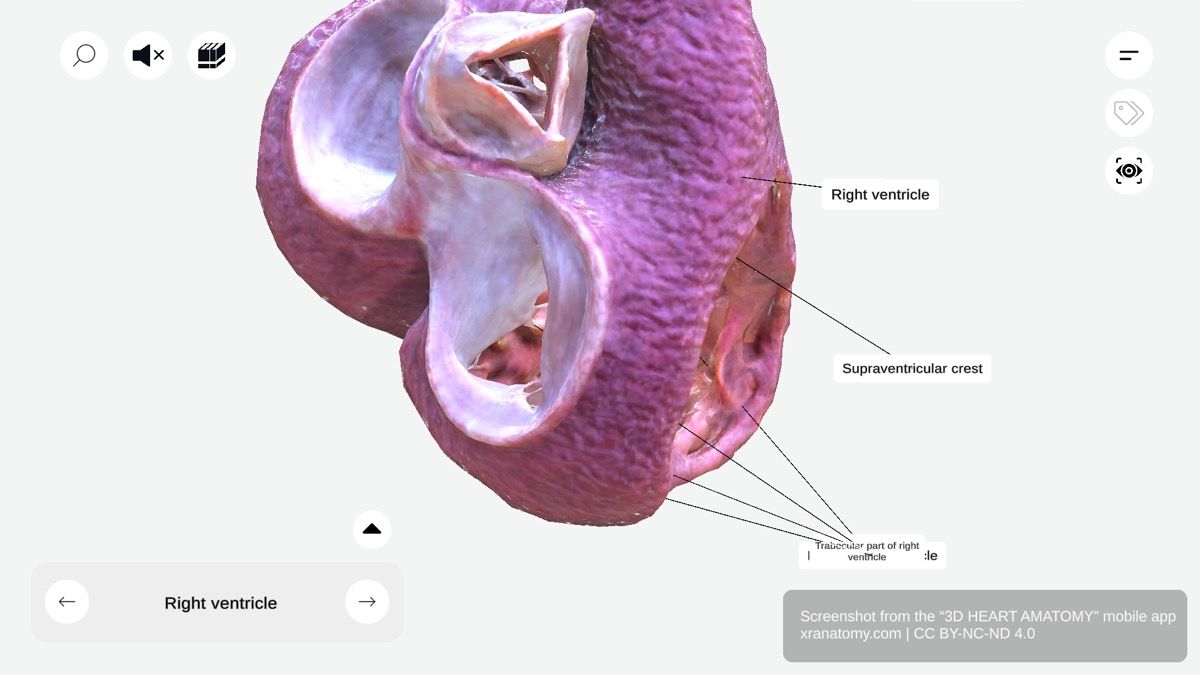
Trabecular Part of Right Ventricle, Preview from the app.
The trabecular part is characterized by a network of muscular ridges. It is thinner than the other components and extends down to your cardiac apex. Its key feature is the trabeculae carneae, the muscular ridges lining the ventricular wall.
Trabeculae Carneae
The trabeculae carneae are muscular ridges on the ventricular wall with coarse trabeculations. They increase the surface area of the ventricular wall and enhance your heart's contractile ability. They also contribute to efficient blood flow.
SEPTOMARGINAL TRABECULA
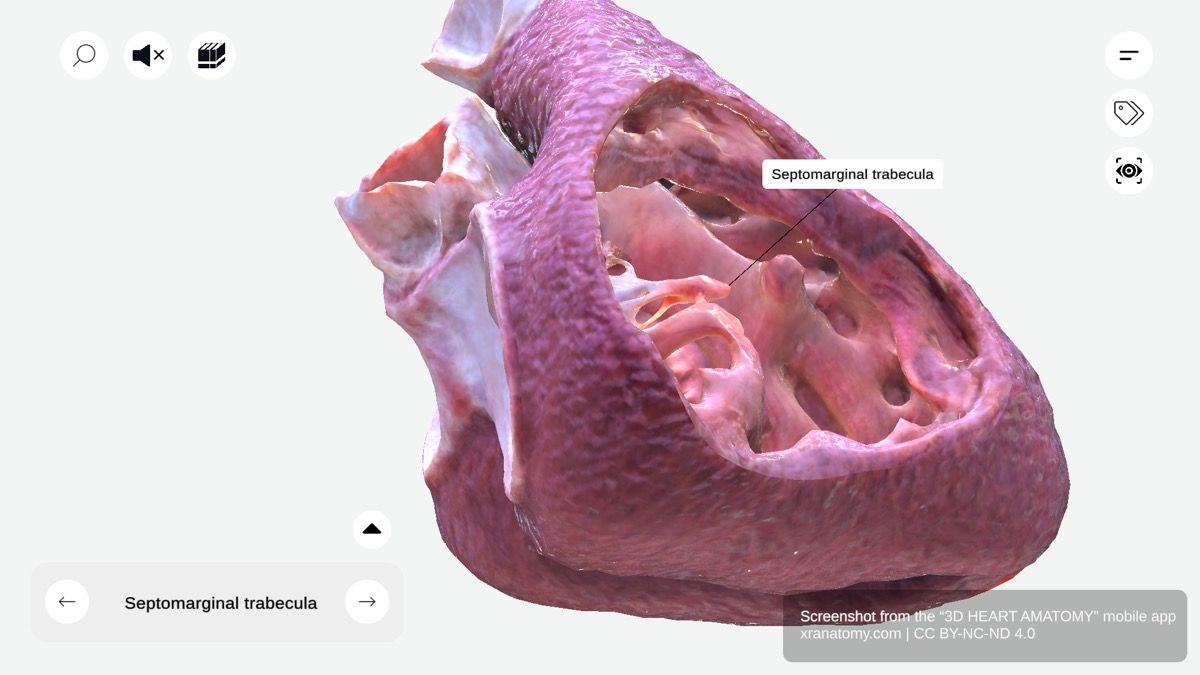
Septomarginal Trabecula (Moderator Band), Preview from the app.
The septomarginal trabecula, also known as the moderator band, is a significant muscular band that extends from your interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle. It contains part of the right bundle branch and facilitates coordinated ventricular contraction in your heart. The septomarginal trabecula divides into two limbs: the parietal limb and the anterior limb.
Divisions
The septomarginal trabecula has two divisions: the parietal limb and the anterior limb.
Parietal Limb
The parietal limb, also called the posteroinferior limb, proceeds posteriorly and supports the muscular septum. The medial papillary muscle typically originates here. This limb contributes to tricuspid valve stability and function.
Anterior Limb
The anterior limb runs to the pulmonary valve leaflet attachment. It is integral to right ventricular structure and ensures proper outflow tract alignment and function.
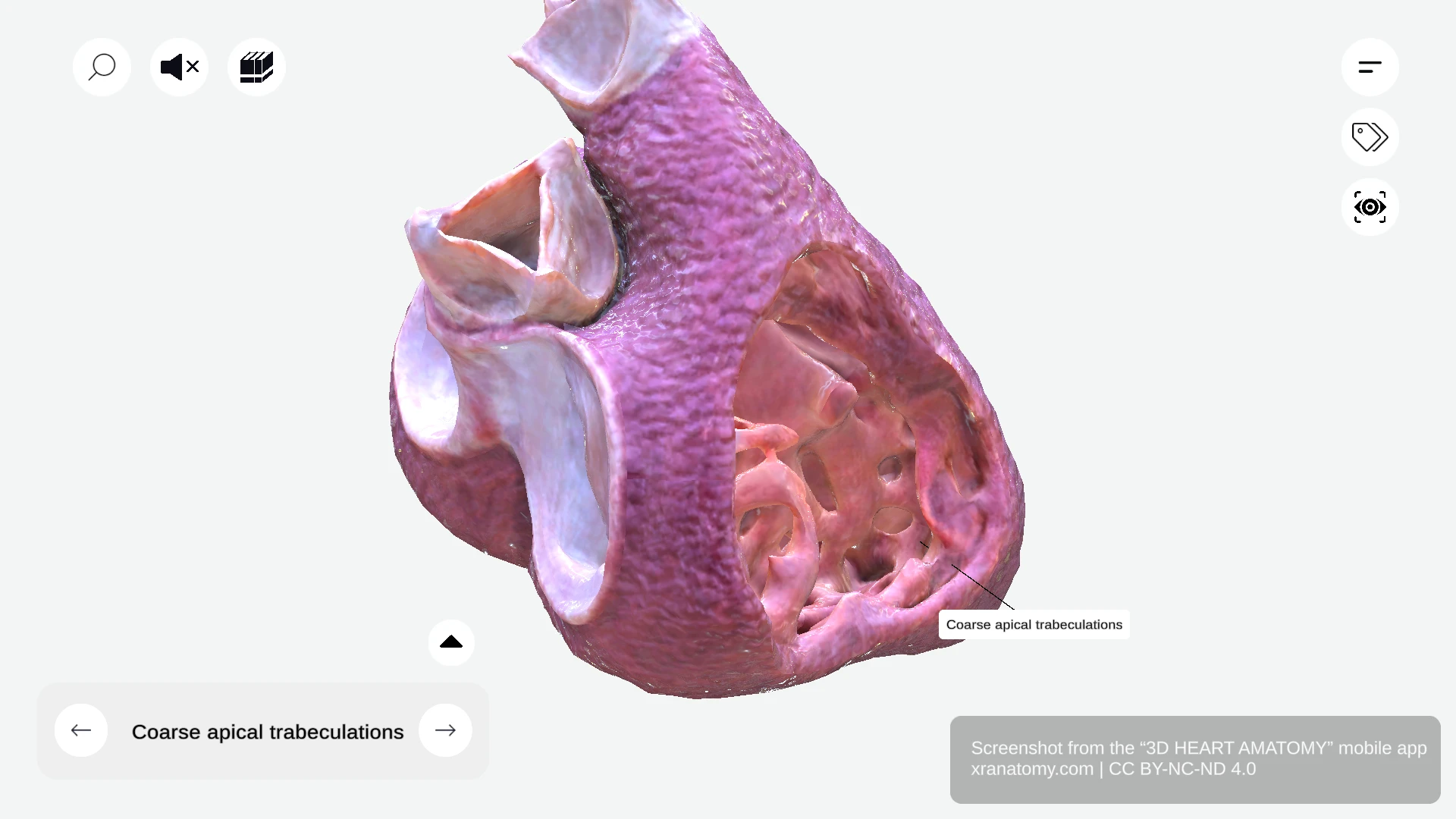
APICAL TRABECULATIONS
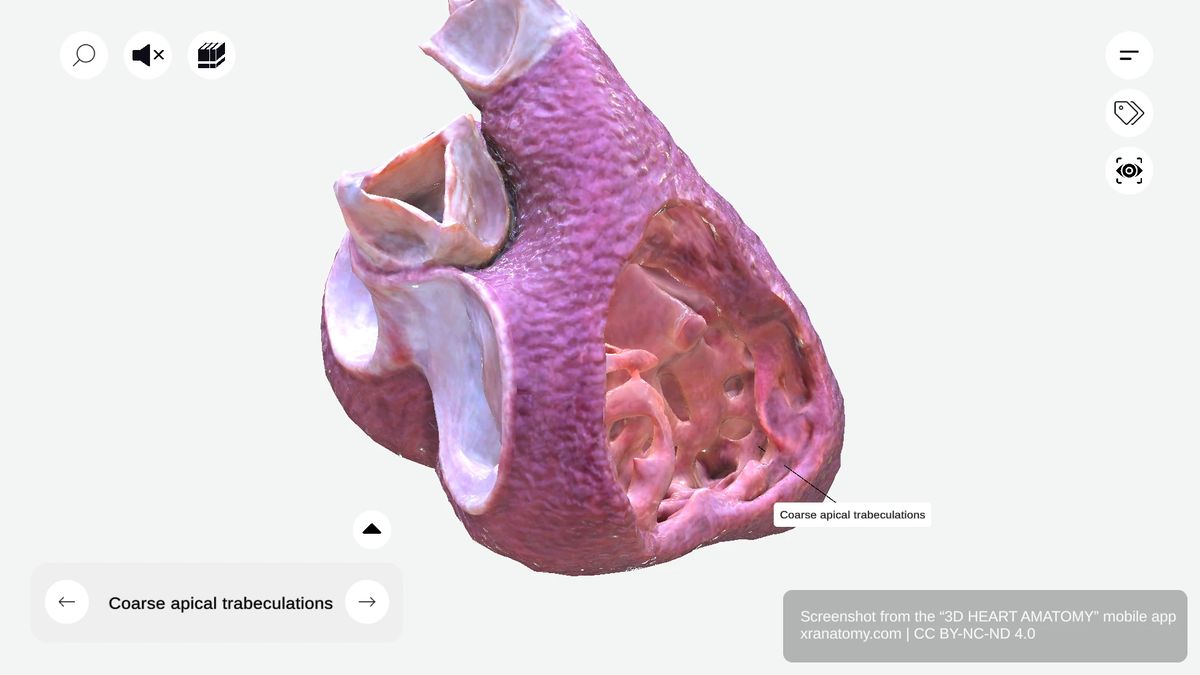
Coarse Apical Trabeculations
The coarse apical trabeculations are robust muscle bundles at the right ventricular apex. They contrast with the finer trabeculations of the left ventricle. These trabeculations are vital for mechanical efficiency during your heart's contraction.
PAPILLARY MUSCLES OF RIGHT VENTRICLE
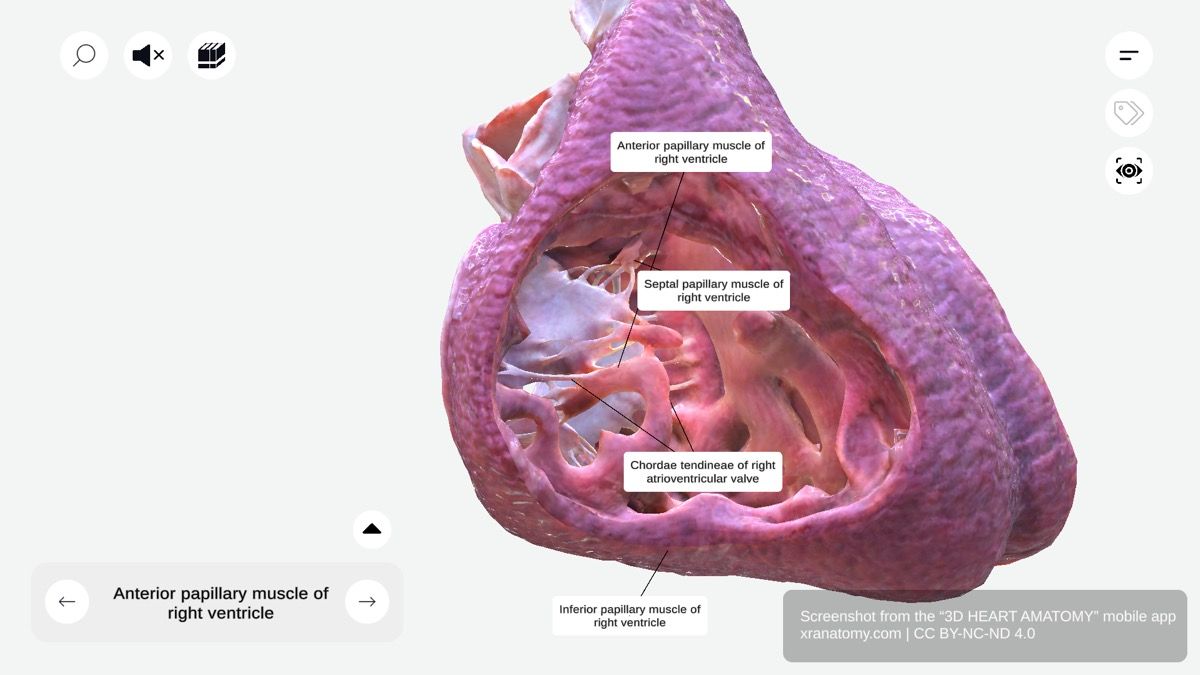
Papillary Muscles of Right Ventricle, Preview from the app.
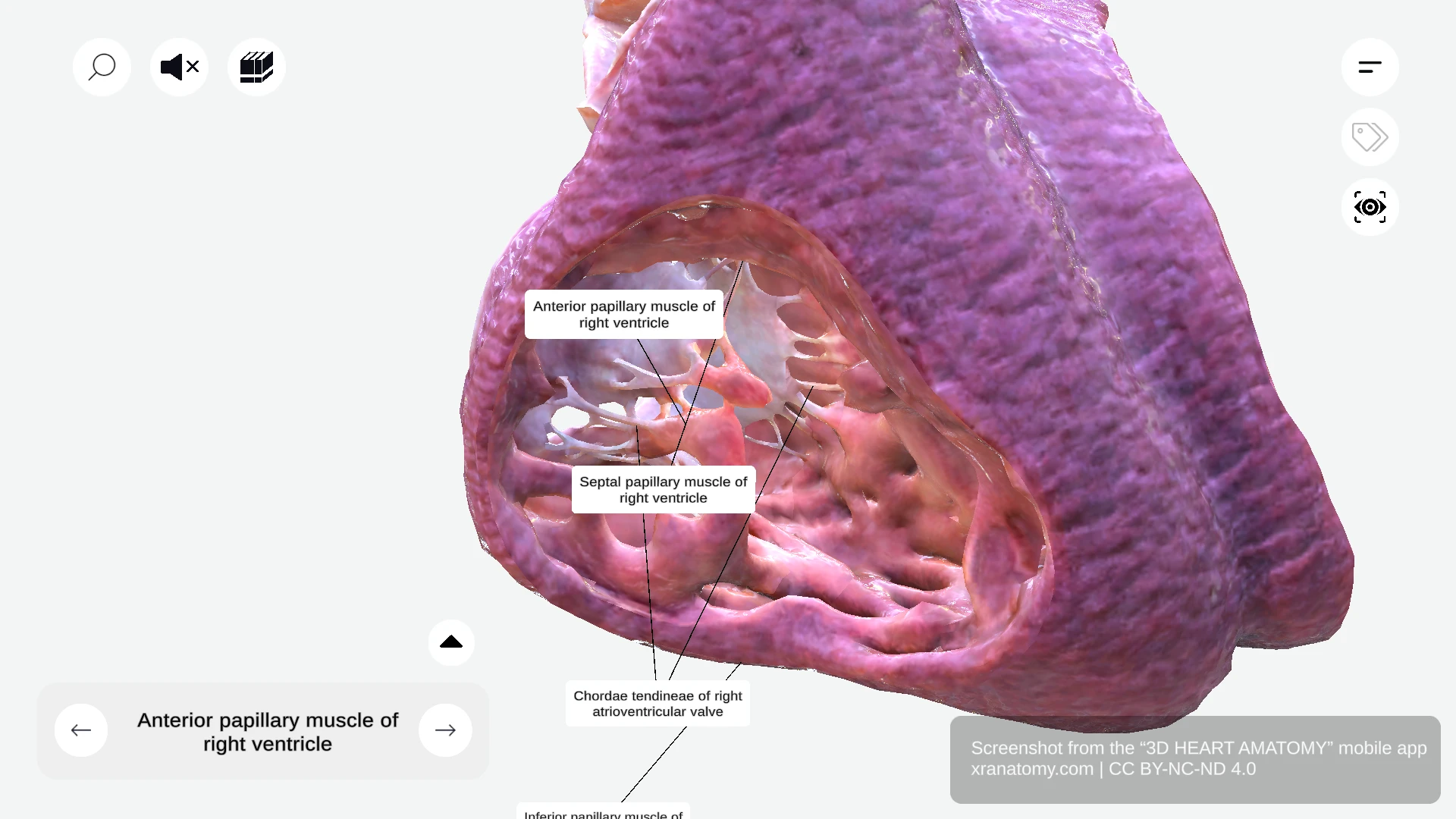
Papillary muscles are conical muscular projections that extend into the ventricular lumen. They connect to your tricuspid valve leaflets via chordae tendineae, prevent valve prolapse during ventricular contraction, and anchor your valve leaflets in position. The right ventricle has three primary papillary muscles: the anterior papillary muscle, the inferior papillary muscle, and the septal papillary muscle.
Three Primary Papillary Muscles
Your right ventricle contains three primary papillary muscles: the anterior papillary muscle, the inferior papillary muscle, and the septal papillary muscle.
Anterior Papillary Muscle
The anterior papillary muscle is the largest and most significant of the three. It originates from the anterior wall of your right ventricle and is supported by the septomarginal trabecula. It connects to the anterior and posterior tricuspid cusps.
Inferior Papillary Muscle
The inferior papillary muscle, also called the posterior papillary muscle, arises from the inferior wall of your right ventricle. It attaches to the posterior and septal tricuspid cusps and aids leaflet stabilization during contraction.
Septal Papillary Muscle
The septal papillary muscle is the smallest of the three and is variable in presence and size. It originates from the interventricular septum and connects to the anterior and septal tricuspid cusps.
CHORDAE TENDINEAE OF RIGHT VENTRICLE
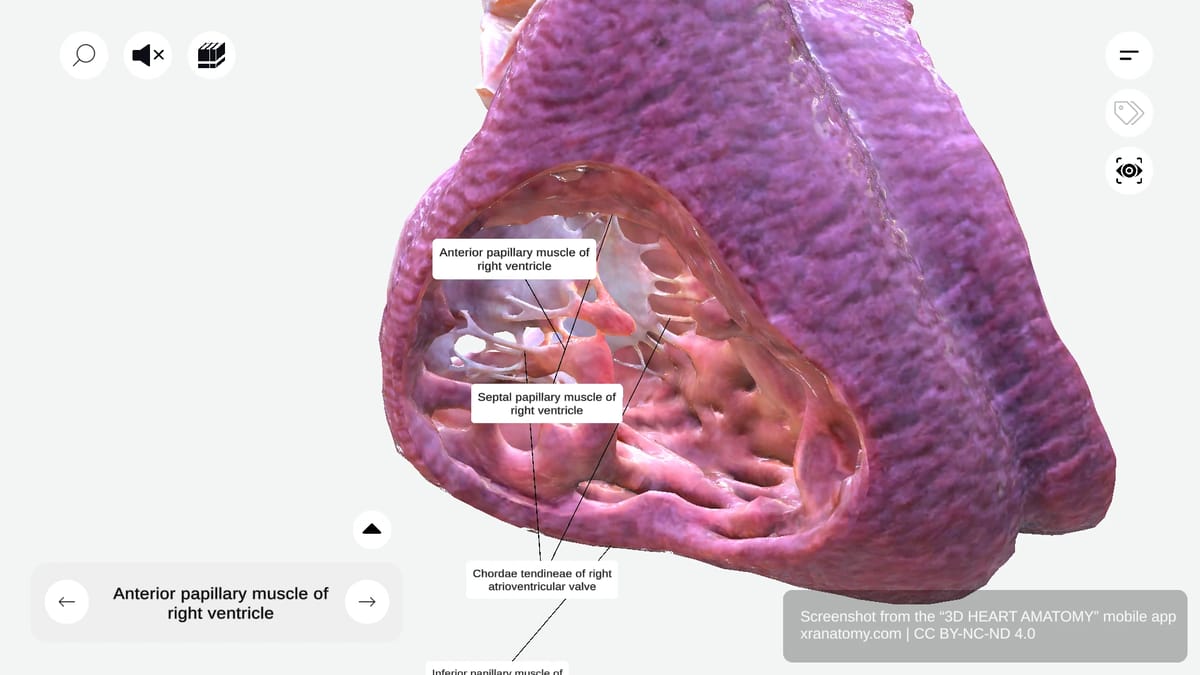
The chordae tendineae are fibrous cords that link your papillary muscles to valve leaflets. They prevent leaflet inversion into the atrium during systole, maintain efficient valve closure, and prevent regurgitation. A related structure, the chordae tendineae spuriae, connects wall to wall rather than to valve leaflets.
Chordae Tendineae Spuriae
The chordae tendineae spuriae, also known as false chordae, connect ventricular wall to ventricular wall or papillary muscles. They do not attach to valve leaflets.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What are the three main components of the right ventricle?
Reveal Answer
The inlet, the trabecular part, and the outlet (conus arteriosus).
2. What does the septomarginal trabecula contain, and what is its function?
Reveal Answer
It contains part of the right bundle branch and facilitates coordinated ventricular contraction. It extends from the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle.
3. Name the three papillary muscles of the right ventricle and identify which is the largest.
Reveal Answer
The anterior papillary muscle (largest and most significant), the inferior (posterior) papillary muscle, and the septal papillary muscle (smallest and variable).
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you understand the right ventricle, the next page covers the Left Ventricle. You will explore how this chamber pumps oxygenated blood to your entire body, including its trabecular part, inlet, papillary muscles, chordae tendineae, and the aortic vestibule.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Gray H, Lewis W. Angiology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918. p. 526–542.
2. Gosling JA, Harris PF, Humpherson JR, Whitmore I, Willan PLT. Human anatomy: color atlas and textbook. 6th ed. 2017. 45–58 p.
3. Anderson RH, Spicer DE, Hlavacek AM, Cook AC, Backer CL. (2013). Anatomy of the cardiac chambers. In Wilcox’s Surgical Anatomy of the Heart (4th ed., pp. 13–50). Cambridge University Press.
4. Fritsch H, Kuehnel W. Color Atlas of Human Anatomy. Vol. Volume 2, Color Atlas and Textbook of Human Anatomy. 2005. 10–42 p.
5. Moore K, Dalley A, Agur A. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Vol. 7ed, Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 2014. 132–151 p.
6. Ho SYen. Anatomy for Cardiac Electrophysiologists: A Practical Handbook. Cardiotext Pub; 2012. 5–27 p.
7. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
8. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.