RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →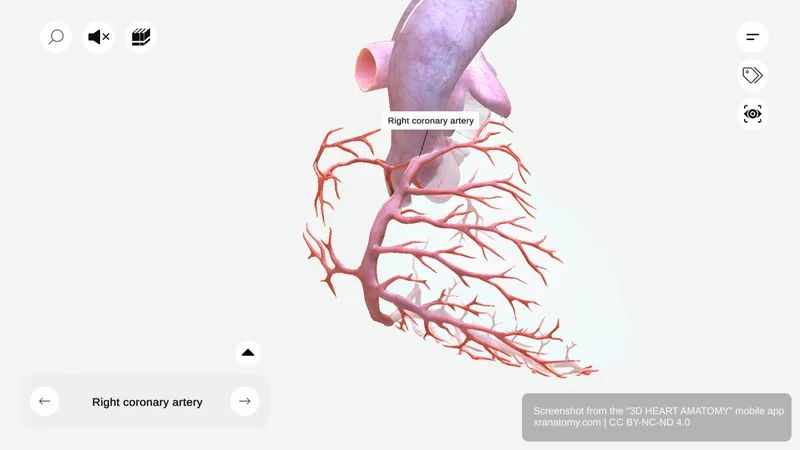
Right Coronary Artery - Overview, Preview from the app.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The right coronary artery is one of two main arteries that deliver oxygenated blood to your heart. It supplies the right side of your heart and gives off branches that reach your cardiac conduction system, including the SA node and AV node. Understanding its course and branching pattern helps you see how your heart maintains its own blood supply.
RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY
Origin and Course
The right coronary artery is one of two main arterial branches from your aorta. It originates from the right aortic sinus and courses along the atrioventricular groove. It generally supplies the right side of your heart.
Branches
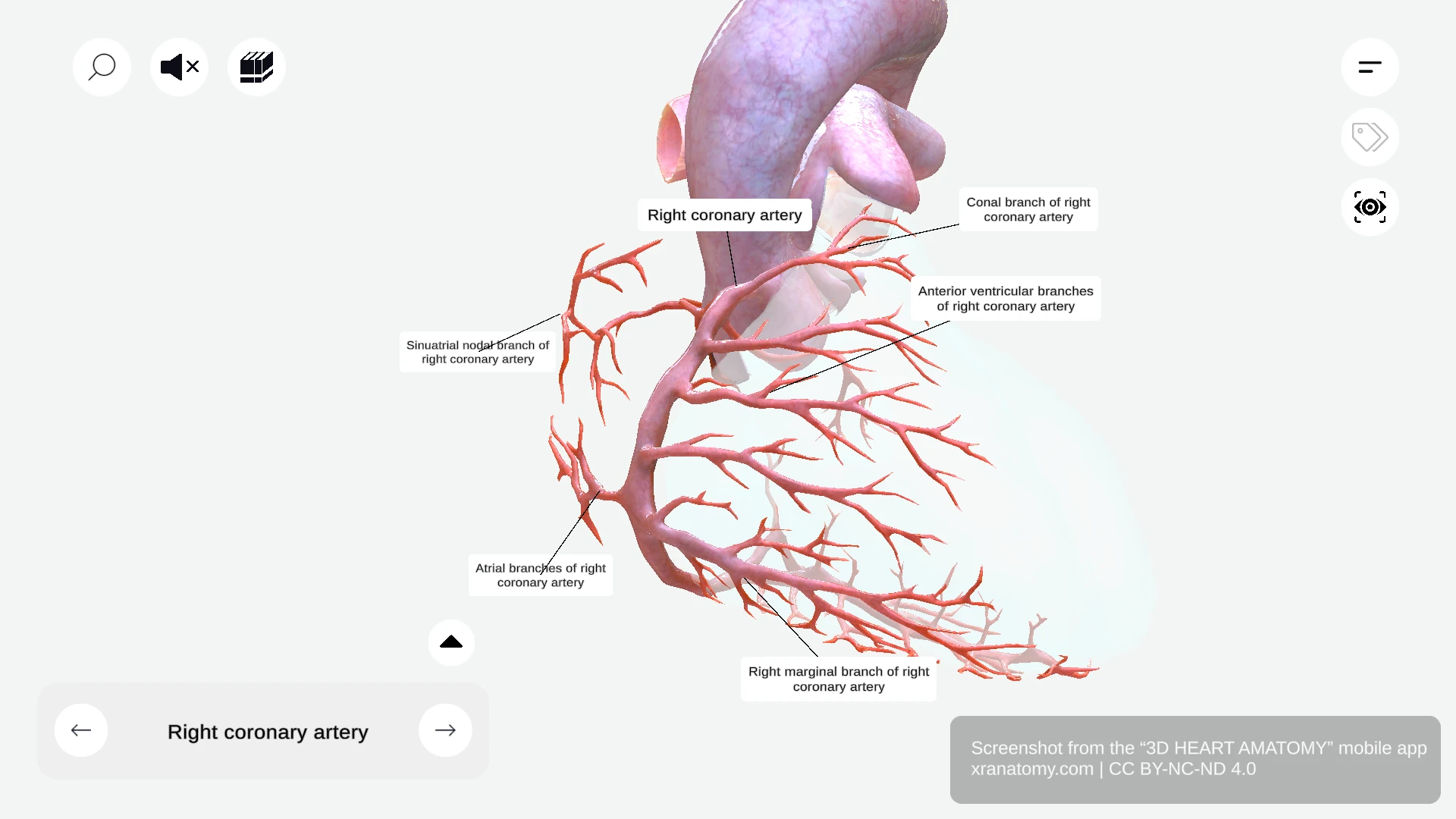
The right coronary artery gives off seven branches: the conal branch, sinu-atrial nodal branch, atrial branches, anterior ventricular branches, right marginal branch, inferior interventricular artery, and atrioventricular nodal branch.
BRANCHES OF RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY
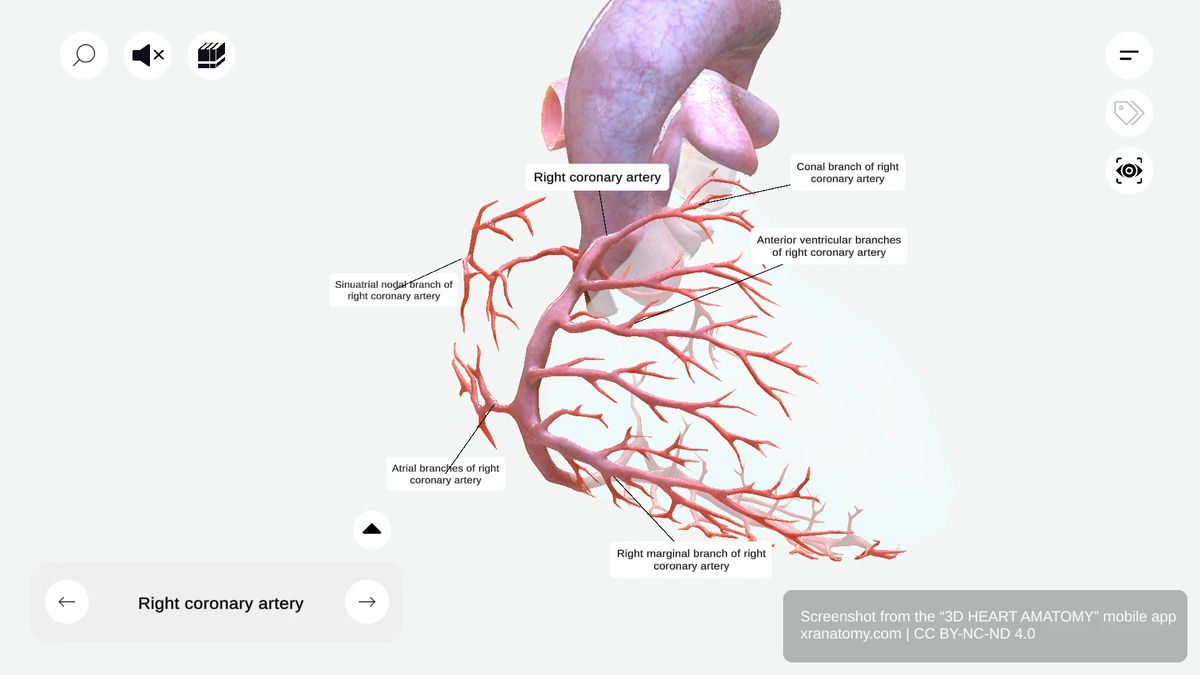
The right coronary artery gives off several branches as it courses along the atrioventricular groove. These include the conal branch supplying your right ventricular outflow tract, the sinu-atrial nodal branch supplying your heart's natural pacemaker, the atrial branches perfusing your right atrium, the anterior ventricular branches supplying the anterior right ventricle, and the right marginal branch supplying your outer right ventricular wall.
Conal Branch
The conal branch, also called the conus arteriosus artery, runs toward the conus arteriosus. It supplies your right ventricular outflow tract.
Sinu-atrial Nodal Branch
The sinu-atrial nodal branch supplies your sinoatrial node, the heart's natural pacemaker. It arises from the RCA in approximately 55-60% of individuals. In 35-40% of individuals, this artery arises from the left circumflex artery instead. It encircles the superior vena cava and may course clockwise or counterclockwise around the SVC.
Atrial Branches
The atrial branches supply your right atrium. They are typically responsible for right atrial perfusion.
Anterior Ventricular Branches
The anterior ventricular branches supply your right ventricle. They perfuse the anterior portion of your right ventricle.
Right Marginal Branch
The right marginal branch is a significant branch of the right coronary artery. It follows the margin of your heart and supplies your outer right ventricular wall.
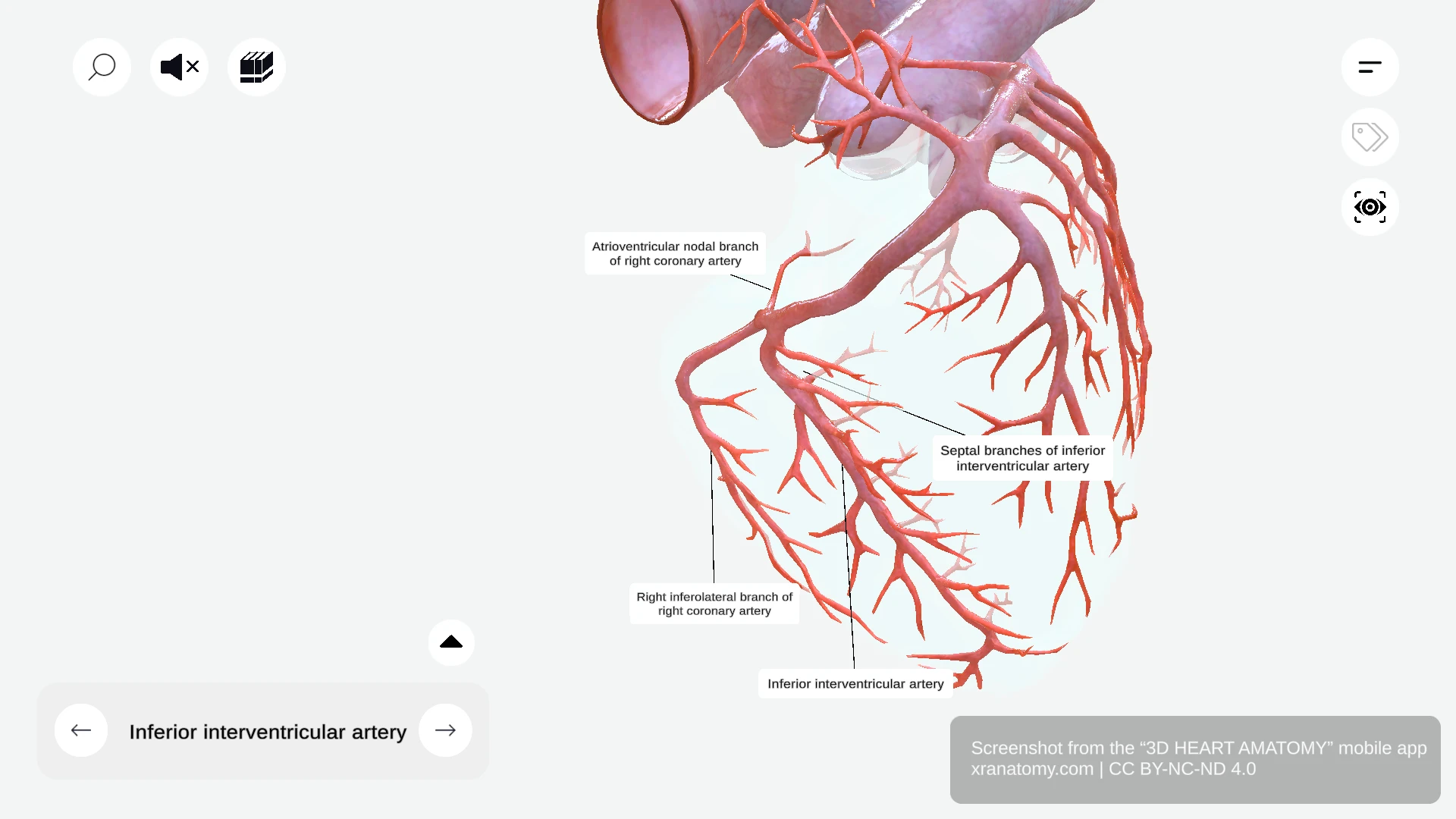
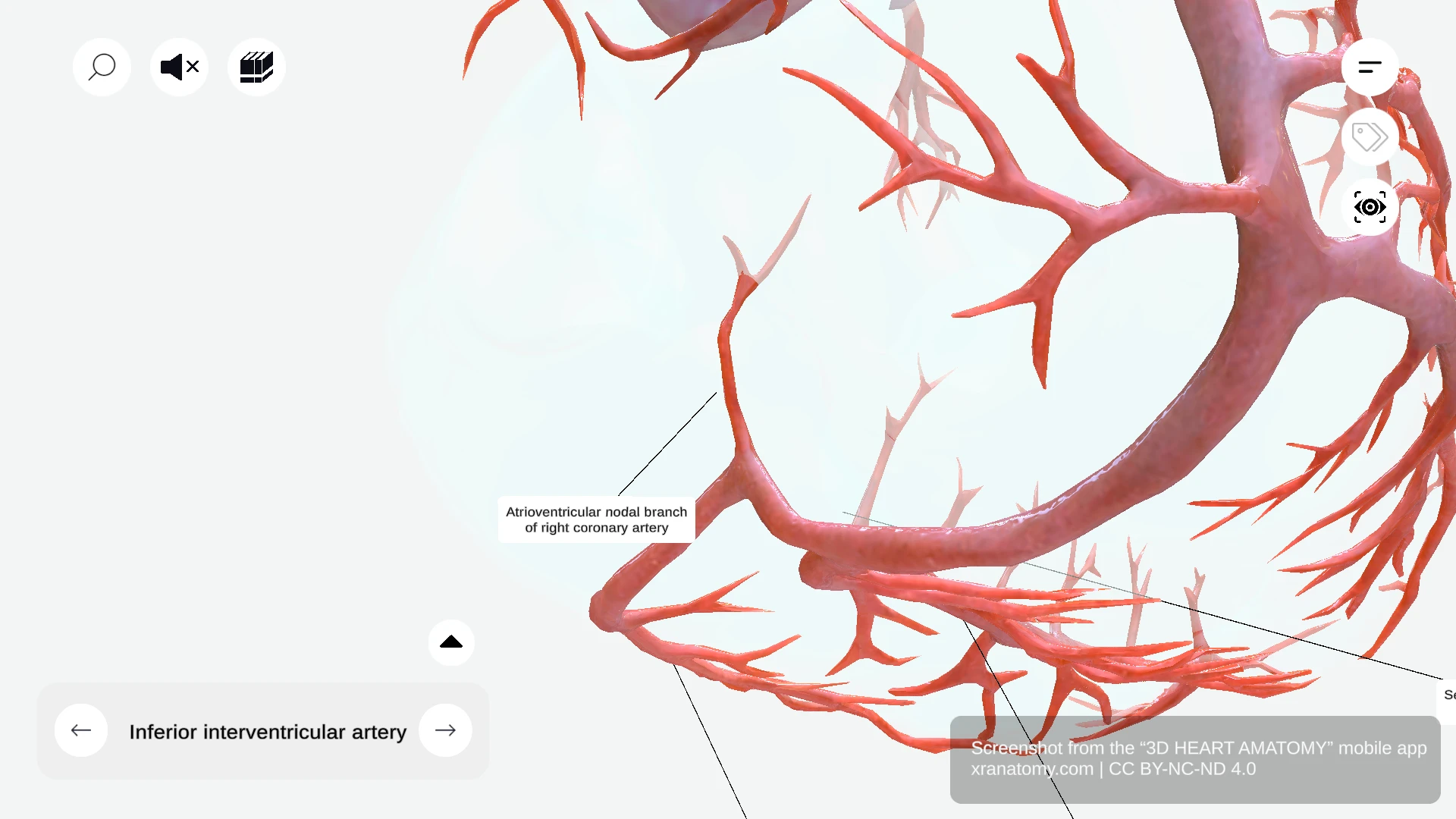
INFERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR ARTERY
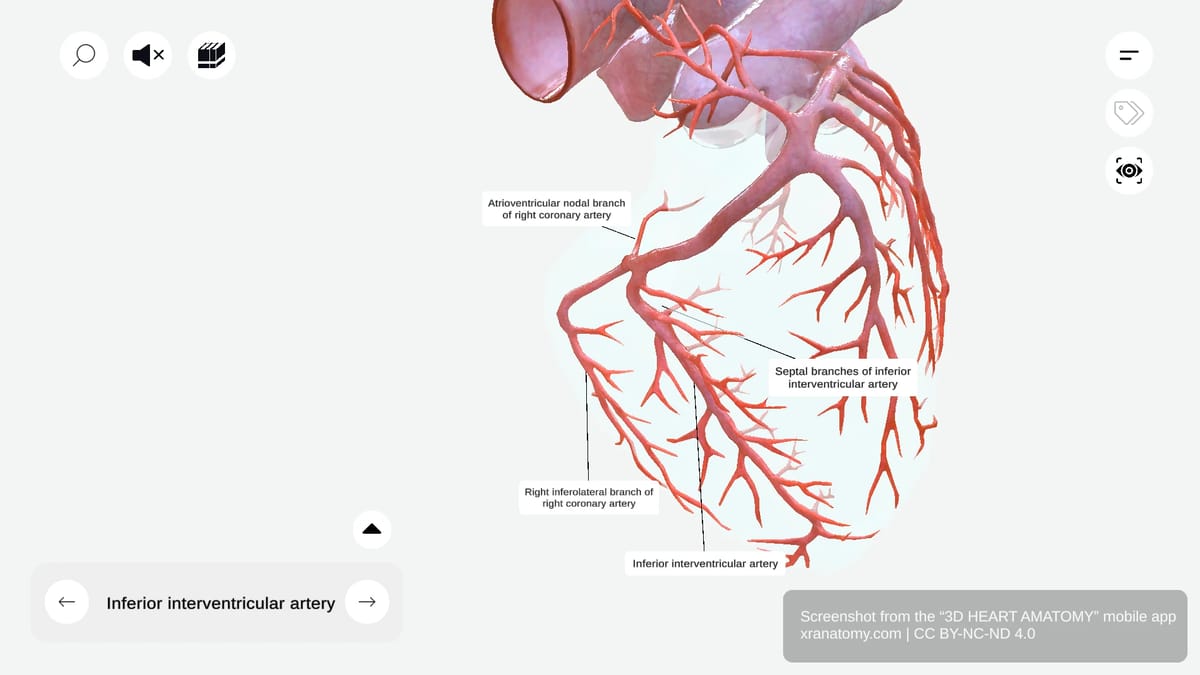
The inferior interventricular artery, also known as the posterior descending artery, runs along the inferior interventricular groove. It gives off septal branches that supply your interventricular septum.
Septal Branches
The septal branches originate from the inferior interventricular artery. They supply your interventricular septum.
ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODAL BRANCH
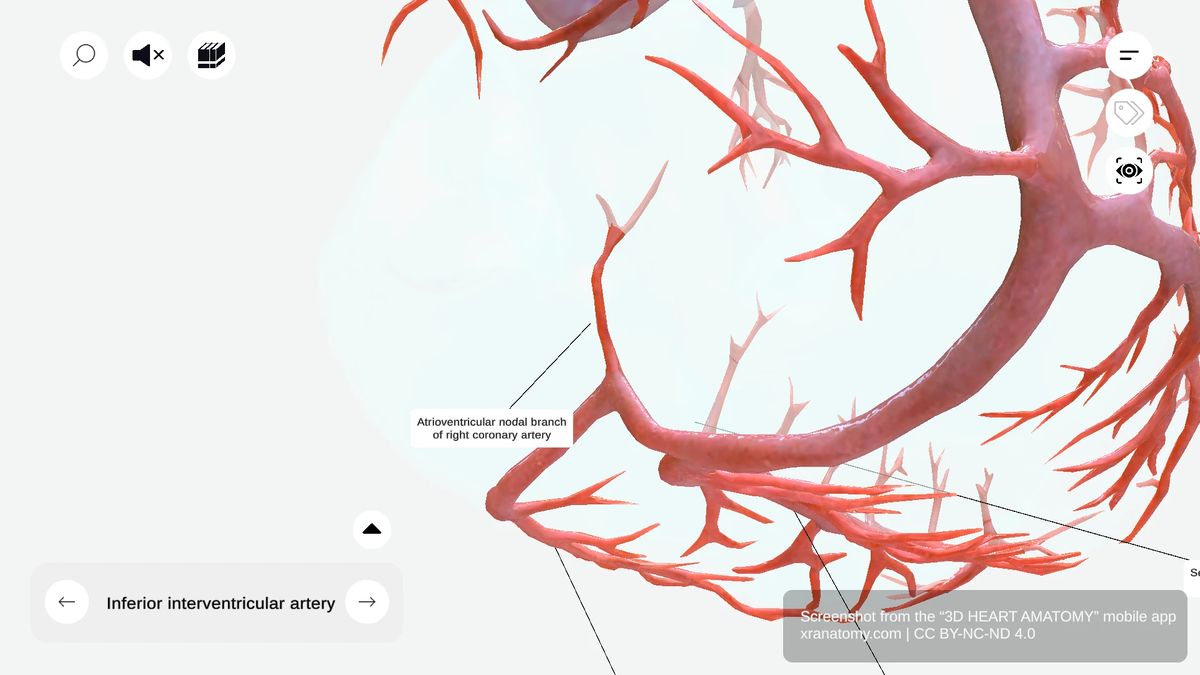
The atrioventricular nodal branch usually arises from the right coronary artery. It supplies the AV node, a key component of your cardiac conduction system.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Where does the right coronary artery originate, and what groove does it course along?
Reveal Answer
It originates from the right aortic sinus and courses along the atrioventricular groove.
2. In what percentage of individuals does the sinu-atrial nodal branch arise from the RCA?
Reveal Answer
Approximately 55-60% of individuals. In 35-40%, it arises from the left circumflex artery instead.
3. What is the inferior interventricular artery also known as, and what does it give off?
Reveal Answer
It is also known as the posterior descending artery. It gives off septal branches that supply the interventricular septum.
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you understand the right coronary artery and its branches, the next page covers the Left Coronary Artery. You will explore how it originates from the left aortic sinus and bifurcates into the anterior interventricular artery (LAD) and the circumflex artery to supply the left side of your heart.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Gray H, Lewis W. Angiology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918. p. 526–542.
2. Gosling JA, Harris PF, Humpherson JR, Whitmore I, Willan PLT. Human anatomy: color atlas and textbook. 6th ed. 2017. 45–58 p.
3. Anderson RH, Spicer DE, Hlavacek AM, Cook AC, Backer CL. (2013). Anatomy of the cardiac chambers. In Wilcox’s Surgical Anatomy of the Heart (4th ed., pp. 13–50). Cambridge University Press.
4. Fritsch H, Kuehnel W. Color Atlas of Human Anatomy. Vol. Volume 2, Color Atlas and Textbook of Human Anatomy. 2005. 10–42 p.
5. Moore K, Dalley A, Agur A. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Vol. 7ed, Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 2014. 132–151 p.
6. Ho SYen. Anatomy for Cardiac Electrophysiologists: A Practical Handbook. Cardiotext Pub; 2012. 5–27 p.
7. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
8. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.